Neuropilin-1high monocytes protect against neonatal inflammation
- PMID: 38632385
- PMCID: PMC11143335
- DOI: 10.1038/s41423-024-01157-7
Neuropilin-1high monocytes protect against neonatal inflammation
Abstract
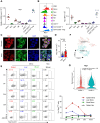
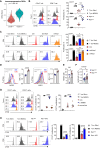
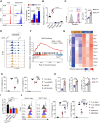
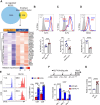
Neonates are susceptible to inflammatory disorders such as necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) due to their immature immune system. The timely appearance of regulatory immune cells in early life contributes to the control of inflammation in neonates, yet the underlying mechanisms of which remain poorly understood. In this study, we identified a subset of neonatal monocytes characterized by high levels of neuropilin-1 (Nrp1), termed Nrp1high monocytes. Compared with their Nrp1low counterparts, Nrp1high monocytes displayed potent immunosuppressive activity. Nrp1 deficiency in myeloid cells aggravated the severity of NEC, whereas adoptive transfer of Nrp1high monocytes led to remission of NEC. Mechanistic studies showed that Nrp1, by binding to its ligand Sema4a, induced intracellular p38-MAPK/mTOR signaling and activated the transcription factor KLF4. KLF4 transactivated Nos2 and enhanced the production of nitric oxide (NO), a key mediator of immunosuppression in monocytes. These findings reveal an important immunosuppressive axis in neonatal monocytes and provide a potential therapeutic strategy for treating inflammatory disorders in neonates.
Keywords: Infant immunity; Inflammation; Monocytes; Neuropilin-1.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to CSI and USTC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. J.Z. is an editorial board member of Cellular & Molecular Immunology, but she has not been involved in the peer review or the decision-making of the article.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81925018/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82130049/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82001660/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 2021M692406/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

