Multi-ancestry meta-analysis of tobacco use disorder identifies 461 potential risk genes and reveals associations with multiple health outcomes
- PMID: 38632388
- PMCID: PMC11199106
- DOI: 10.1038/s41562-024-01851-6
Multi-ancestry meta-analysis of tobacco use disorder identifies 461 potential risk genes and reveals associations with multiple health outcomes
Abstract
Tobacco use disorder (TUD) is the most prevalent substance use disorder in the world. Genetic factors influence smoking behaviours and although strides have been made using genome-wide association studies to identify risk variants, most variants identified have been for nicotine consumption, rather than TUD. Here we leveraged four US biobanks to perform a multi-ancestral meta-analysis of TUD (derived via electronic health records) in 653,790 individuals (495,005 European, 114,420 African American and 44,365 Latin American) and data from UK Biobank (ncombined = 898,680). We identified 88 independent risk loci; integration with functional genomic tools uncovered 461 potential risk genes, primarily expressed in the brain. TUD was genetically correlated with smoking and psychiatric traits from traditionally ascertained cohorts, externalizing behaviours in children and hundreds of medical outcomes, including HIV infection, heart disease and pain. This work furthers our biological understanding of TUD and establishes electronic health records as a source of phenotypic information for studying the genetics of TUD.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Smoller is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Sensorium Therapeutics (with equity) and has received grant support from Biogen, Inc. He is PI of a collaborative study of the genetics of depression and bipolar disorder sponsored by 23andMe for which 23andMe provides analysis time as in-kind support but no payments. Dr. Kranzler is a member of advisory boards for Clearmind Medicine, Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, Sophrosyne Pharmaceuticals, and Enthion Pharmaceuticals; a consultant to Sobrera Pharmaceuticals; the recipient of research funding and medication supplies for an investigator-initiated study from Alkermes; a member of the American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology’s Alcohol Clinical Trials Initiative, which was supported in the last three years by Alkermes, Dicerna, Ethypharm, Lundbeck, Mitsubishi, Otsuka, and Pear Therapeutics; and with Dr. Gelernter, a holder of U.S. patent 10,900,082 titled: “Genotype-guided dosing of opioid agonists,” issued 26 January 2021. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
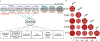

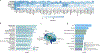

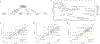

Update of
-
Multi-ancestry meta-analysis of tobacco use disorder prioritizes novel candidate risk genes and reveals associations with numerous health outcomes.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 18:2023.03.27.23287713. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.27.23287713. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Hum Behav. 2024 Jun;8(6):1177-1193. doi: 10.1038/s41562-024-01851-6. PMID: 37034728 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Health Effects of Cigarette Smoking. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/fact_sheets/health_effects/e... (2021).
-
- WHO. The top 10 causes of death. World Health Organization; https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death.
-
- Benowitz NL & Liakoni E Tobacco use disorder and cardiovascular health. Addiction 117, 1128–1138 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- T32IR5226/Tobacco-Related Disease Research Program (TRDRP)
- U01 DA041120/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32HG010464/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
- I01 BX004820/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 DA042090/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DA051759/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041025/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041117/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T29KT0526/Tobacco-Related Disease Research Program (TRDRP)
- U01 DA041174/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA041147/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA050721/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001878/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- DP1DA054394/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041093/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01DA051759/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG010464/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA054869/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50DA037844/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- 5R01DA054869/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- U24 DA041123/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025141/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041134/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041022/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX001849/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- U01 DA041156/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH121924/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AA030083/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD074711/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA022537/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 GM092618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041089/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 AA018755/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DA054394/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041106/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM115305/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AA028292/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA051913/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041028/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103537/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041048/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006378/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA037844/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041148/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA015416/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS032830/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004798/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 AA008401/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH113362/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AA030083/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)

