Neural crest origin of sympathetic neurons at the dawn of vertebrates
- PMID: 38632395
- PMCID: PMC11391089
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07297-0
Neural crest origin of sympathetic neurons at the dawn of vertebrates
Abstract
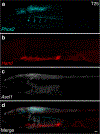
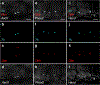
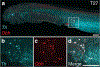
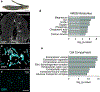
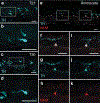
The neural crest is an embryonic stem cell population unique to vertebrates1 whose expansion and diversification are thought to have promoted vertebrate evolution by enabling emergence of new cell types and structures such as jaws and peripheral ganglia2. Although jawless vertebrates have sensory ganglia, convention has it that trunk sympathetic chain ganglia arose only in jawed vertebrates3-8. Here, by contrast, we report the presence of trunk sympathetic neurons in the sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus, an extant jawless vertebrate. These neurons arise from sympathoblasts near the dorsal aorta that undergo noradrenergic specification through a transcriptional program homologous to that described in gnathostomes. Lamprey sympathoblasts populate the extracardiac space and extend along the length of the trunk in bilateral streams, expressing the catecholamine biosynthetic pathway enzymes tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine β-hydroxylase. CM-DiI lineage tracing analysis further confirmed that these cells derive from the trunk neural crest. RNA sequencing of isolated ammocoete trunk sympathoblasts revealed gene profiles characteristic of sympathetic neuron function. Our findings challenge the prevailing dogma that posits that sympathetic ganglia are a gnathostome innovation, instead suggesting that a late-developing rudimentary sympathetic nervous system may have been characteristic of the earliest vertebrates.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Le Douarin N The Neural Crest. (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1982).
-
- Botar J Evolution and general anatomy of the autonomic nervous system. Gegenbaurs Morphol Jahrb 120, 271–279 (1974). - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G Evolution of the autonomic innervation of visceral and cardiovascular systems in vertebrates. Pharmacol Rev 21, 247–324 (1969). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

