Neuroimaging of posttraumatic stress disorder in adults and youth: progress over the last decade on three leading questions of the field
- PMID: 38632413
- PMCID: PMC11449801
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-024-02558-w
Neuroimaging of posttraumatic stress disorder in adults and youth: progress over the last decade on three leading questions of the field
Abstract
Almost three decades have passed since the first posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) neuroimaging study was published. Since then, the field of clinical neuroscience has made advancements in understanding the neural correlates of PTSD to create more efficacious treatment strategies. While gold-standard psychotherapy options are available, many patients do not respond to them, prematurely drop out, or never initiate treatment. Therefore, elucidating the neurobiological mechanisms that define the disorder can help guide clinician decision-making and develop individualized mechanisms-based treatment options. To this end, this narrative review highlights progress made in the last decade in adult and youth samples on three outstanding questions in PTSD research: (1) Which neural alterations serve as predisposing (pre-exposure) risk factors for PTSD development, and which are acquired (post-exposure) alterations? (2) Which neural alterations can predict treatment outcomes and define clinical improvement? and (3) Can neuroimaging measures be used to define brain-based biotypes of PTSD? While the studies highlighted in this review have made progress in answering the three questions, the field still has much to do before implementing these findings into clinical practice. Overall, to better answer these questions, we suggest that future neuroimaging studies of PTSD should (A) utilize prospective longitudinal designs, collecting brain measures before experiencing trauma and at multiple follow-up time points post-trauma, taking advantage of multi-site collaborations/consortiums; (B) collect two scans to explore changes in brain alterations from pre-to-post treatment and compare changes in neural activation between treatment groups, including longitudinal follow up assessments; and (C) replicate brain-based biotypes of PTSD. By synthesizing recent findings, this narrative review will pave the way for personalized treatment approaches grounded in neurobiological evidence.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

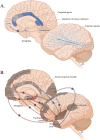
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5TM, 5th ed. Arlington, VA, US: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.; 2013. xliv, 947 p. (Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5TM, 5th ed).
-
- Paganin W, Signorini S. Biomarkers of post-traumatic stress disorder from emotional trauma: a systematic review. Eur J Trauma Dissociation. 2023;7:100328.
-
- Bonanno GA. Loss, trauma, and human resilience: Have we underestimated the human capacity to thrive after extremely aversive events? Psychol Trauma Theory Res Pr Policy. 2008;S:101–13. - PubMed
-
- Galatzer-Levy IR, Huang SH, Bonanno GA. Trajectories of resilience and dysfunction following potential trauma: a review and statistical evaluation. Clin Psychol Rev. 2018;63:41–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- K99 AA031333/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH125786/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32MH125786/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- K99AA031333/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

