Tissue-specific atlas of trans-models for gene regulation elucidates complex regulation patterns
- PMID: 38632500
- PMCID: PMC11022497
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-10317-y
Tissue-specific atlas of trans-models for gene regulation elucidates complex regulation patterns
Abstract
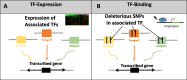
Background: Deciphering gene regulation is essential for understanding the underlying mechanisms of healthy and disease states. While the regulatory networks formed by transcription factors (TFs) and their target genes has been mostly studied with relation to cis effects such as in TF binding sites, we focused on trans effects of TFs on the expression of their transcribed genes and their potential mechanisms.
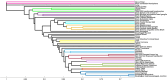
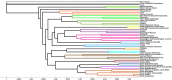
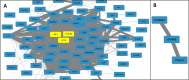
Results: We provide a comprehensive tissue-specific atlas, spanning 49 tissues of TF variations affecting gene expression through computational models considering two potential mechanisms, including combinatorial regulation by the expression of the TFs, and by genetic variants within the TF. We demonstrate that similarity between tissues based on our discovered genes corresponds to other types of tissue similarity. The genes affected by complex TF regulation, and their modelled TFs, were highly enriched for pharmacogenomic functions, while the TFs themselves were also enriched in several cancer and metabolic pathways. Additionally, genes that appear in multiple clusters are enriched for regulation of immune system while tissue clusters include cluster-specific genes that are enriched for biological functions and diseases previously associated with the tissues forming the cluster. Finally, our atlas exposes multilevel regulation across multiple tissues, where TFs regulate other TFs through the two tested mechanisms.
Conclusions: Our tissue-specific atlas provides hierarchical tissue-specific trans genetic regulations that can be further studied for association with human phenotypes.
Keywords: Transcription factor polymorphism; Transcriptional regulation; Transcriptome imputation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tissue-Specific Variations in Transcription Factors Elucidate Complex Immune System Regulation.Genes (Basel). 2022 May 23;13(5):929. doi: 10.3390/genes13050929. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35627314 Free PMC article.
-
Computational analysis of tissue-specific combinatorial gene regulation: predicting interaction between transcription factors in human tissues.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(17):4925-36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl595. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16982645 Free PMC article.
-
hTFtarget: A Comprehensive Database for Regulations of Human Transcription Factors and Their Targets.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2020 Apr;18(2):120-128. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2019.09.006. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32858223 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors: Bridge between cell signaling and gene regulation.Proteomics. 2021 Dec;21(23-24):e2000034. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202000034. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 34314098 Review.
-
Coordinated networks of microRNAs and transcription factors with evolutionary perspectives.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;774:169-87. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5590-1_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23377974 Review.
References
-
- Chen C, Jiang L, Shen B, Wang M, Griffin CH, Chinchilli VM, et al. A computational atlas of tissue-specific regulatory networks. Front Syst Biol. 2021;1:764161. doi: 10.3389/fsysb.2021.764161. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

