Study on the differential hepatotoxicity of raw polygonum multiflorum and polygonum multiflorum praeparata and its mechanism
- PMID: 38632548
- PMCID: PMC11022370
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-024-04463-9
Study on the differential hepatotoxicity of raw polygonum multiflorum and polygonum multiflorum praeparata and its mechanism
Abstract
Background: Polygonum multiflorum (PM), a widely used traditional Chinese medicine herb, is divided into two forms, namely raw polygonum multiflorum (RPM) and polygonum multiflorum praeparata (PMP), according to the processing procedure. Emerging data has revealed the differential hepatotoxicity of RPM and PMP, however, its potential mechanism is still unclear.
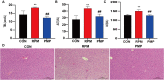
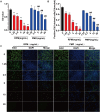
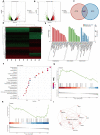
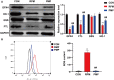
Methods: In our study, we investigated the differential hepatotoxicity of RPM and PMP exerted in C57BL/6 mice. First, sera were collected for biochemical analysis and HE staining was applied to examine the morphological alternation of the liver. Then we treated L02 cells with 5 mg / mL of RPM or PMP. The CCK8 and EdU assays were utilized to observe the viability and proliferation of L02 cells. RNA sequencing was performed to explore the expression profile of L02 cells. Western blotting was performed to detect the expression level of ferroptosis-related protein. Flow cytometry was used to evaluate ROS accumulation.
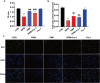
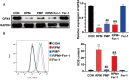
Results: In our study, a significant elevation in serum ALT, AST and TBIL levels was investigated in the RMP group, while no significant differences were observed in the PMP group, compared to that of the CON group. HE staining showed punctate necrosis, inflammatory cell infiltration and structural destruction can be observed in the RPM group, which can be significantly attenuated after processing. In addition, we also found RPM could decrease the viability and proliferation capacity of L02 cells, which can be reversed by ferroptosis inhibitor. RNA sequencing data revealed the adverse effect of PM exerted on the liver is closely associated with ferroptosis. Western blotting assay uncovered the protein level of GPX4, HO-1 and FTL was sharply decreased, while the ROS content was dramatically elevated in L02 cells treated with RPM, which can be partially restored after processing.
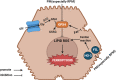
Conclusions: The hepatotoxicity induced by RPM was significantly lower than the PMP, and its potential mechanism is associated with ferroptosis.
Keywords: Ferroptosis; Hepatotoxicity; Polygonum multiflorum; Polygonum multiflorum praeparata; Raw polygonum multiflorum.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhao D S Jiangll, Fan Y X et al. Transcriptome analysis to assess the cholestatic hepatotoxicity induced by Polygoni Multiflori Radix: Up-regulation of key enzymes of cholesterol and bile acid biosynthesis [J]. J Proteom, 2018, 177(40 – 7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

