Heparin-induced DRESS syndrome in a paediatric patient and successful anaesthetic management in cardiovascular bypass surgery: case report
- PMID: 38632589
- PMCID: PMC11022424
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-024-02722-x
Heparin-induced DRESS syndrome in a paediatric patient and successful anaesthetic management in cardiovascular bypass surgery: case report
Abstract
Background: Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome is a severe adverse drug reaction marked by delayed hypersensitivity reactions causing skin and systemic complications. DRESS diagnosis is challenging due to the variety of clinical presentations and symptom overlap with other conditions. The perioperative period in these patients requires precise pharmacological strategies to prevent complications associated with this syndrome. The treatment of DRESS induced by unfractionated heparin during cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) surgery presents some challenges that must be considered when selecting an anticoagulant to avoid side effects. In this case, bivalirudin, a direct thrombin inhibitor, is indicated as an alternative to heparin in patients undergoing CPB. However, in contrast to heparin/protamine, there is no direct reversal agent for bivalirudin.
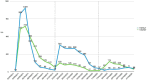
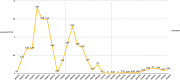
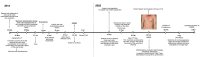
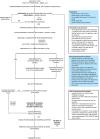
Case presentation: We report the case of an 11-year-old male diagnosed with native aortic valve endocarditis and thrombosis in his left lower extremity. During valvular replacement surgery, systemic unfractionated heparin was administered. Postoperatively, the patient developed fever, eosinophilia and pruritic rash. Warm shock and elevated alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) levels followed, leading to the diagnosis of DRESS syndrome. Treatment with methylprednisolone resulted in complete resolution of symptoms. Seven years later, the patient was readmitted due to insufficient anticoagulation and a thrombus in the prosthetic aortic valve, presenting a recurrent DRESS episode due to the administration of unfractionated heparin, which was later replaced with low-molecular-weight heparin during hospitalization. Treatment with corticosteroids and antihistamines was initiated, resulting in the resolution of this episode. Ultimately, the patient required the Ross procedure. During this intervention the anticoagulation strategy was modified, unfractionated heparin was replaced with bivalirudin during the procedure and fondaparinux was administered during the postoperative period. This resulted in stable transaminases levels and no eosinophilia.
Conclusion: The severity of DRESS Syndrome underscores the importance of early recognition, heightened monitoring, and a comprehensive approach tailored to each patient's needs. This particular case highlights the significance of this approach and may have a substantial clinical impact since it provides alternatives to heparin, such as bivalirudin and fondaparinux, in the anticoagulation strategy of CPB for patients who have a hypersensibility reaction to this medication; thus, enhancing clinical outcomes by minimizing risks linked to adverse drug reactions.
Keywords: Bivalirudin; Cardiopulmonary bypass; Drug hypersensitivity syndrome; Eosinophilia; Heparin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bahçeci S, Can D. Dress syndrome. Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2020;18(1):1–9. doi: 10.21911/aai.444. - DOI
-
- Hiransuthikul A, Rattananupong T, Klaewsongkram J, Rerknimitr P, Pongprutthipan M, Ruxrungtham K. Drug- induced hypersensitivity syndrome/drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DIHS/DRESS): 11 years retrospective study in Thailand. Allergol Int. 2016;65(4):432–8. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2016.04.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

