Spatial and single-cell explorations uncover prognostic significance and immunological functions of mitochondrial calcium uniporter in breast cancer
- PMID: 38632642
- PMCID: PMC11022417
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-024-03327-z
Spatial and single-cell explorations uncover prognostic significance and immunological functions of mitochondrial calcium uniporter in breast cancer
Abstract
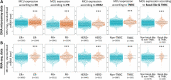
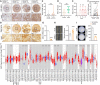
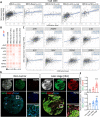
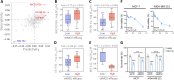
The mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) is a transmembrane protein facilitating the entry of calcium ions into mitochondria from the cell cytosol. Maintaining calcium balance is crucial for enhancing cellular energy supply and regulating cell death. The interplay of calcium balance through MCU and the sodium-calcium exchanger is known, but its regulation in the breast cancer tumor microenvironment remains elusive. Further investigations are warranted to explore MCU's potential in BRCA clinical pathology, tumor immune microenvironment, and precision oncology. Our study, employing a multi-omics approach, identifies MCU as an independent diagnostic biomarker for breast cancer (BRCA), correlated with advanced clinical status and poor overall survival. Utilizing public datasets from GEO and TCGA, we discern differentially expressed genes in BRCA and examine their associations with immune gene expression, overall survival, tumor stage, gene mutation status, and infiltrating immune cells. Spatial transcriptomics is employed to investigate MCU gene expression in various regions of BRCA, while spatial transcriptomics and single-cell RNA-sequencing methods explore the correlation between MCUs and immune cells. Our findings are validated through the analysis of 59 BRCA patient samples, utilizing immunohistochemistry and bioinformatics to examine the relationship between MCU expression, clinicopathological features, and prognosis. The study uncovers the expression of key gene regulators in BRCA associated with genetic variations, deletions, and the tumor microenvironment. Mutations in these regulators positively correlate with different immune cells in six immune datasets, playing a pivotal role in immune cell infiltration in BRCA. Notably, high MCU performance is linked to CD8 + T cells infiltration in BRCA. Furthermore, pharmacogenomic analysis of BRCA cell lines indicates that MCU inactivation is associated with increased sensitivity to specific small molecule drugs. Our findings suggest that MCU alterations may be linked to BRCA progression, unveiling new diagnostic and prognostic implications for MCU in BRCA. The study underscores MCU's role in the tumor immune microenvironment and cell cycle progression, positioning it as a potential tool for BRCA precision medicine and drug screening.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Immune infiltration; MCU; Single-cell RNA-sequencing; Spatial transcriptomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial calcium uniporter as biomarker and therapeutic target for breast cancer: Prognostication, immune microenvironment, epigenetic regulation and precision medicine.J Adv Res. 2025 Apr;70:445-461. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.04.015. Epub 2024 Apr 24. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38663838 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial and single-cell analyses uncover links between ALKBH1 and tumor-associated macrophages in gastric cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Feb 6;24(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03232-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38317214 Free PMC article.
-
The role of LSM1 in breast cancer: Shaping metabolism and tumor-associated macrophage infiltration.Pharmacol Res. 2023 Dec;198:107008. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.107008. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 37995895
-
Single-cell landscape and spatial transcriptomic analysis reveals macrophage infiltration and glycolytic metabolism in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Oct 16;15(20):11298-11312. doi: 10.18632/aging.205128. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37847178 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) complex in cancer.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Aug;470(8):1149-1163. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2162-8. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 29926229 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial transcriptomics in breast cancer: providing insight into tumor heterogeneity and promoting individualized therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 19;15:1499301. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1499301. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39749323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial transcriptomics: a new frontier in accurate localization of breast cancer diagnosis and treatment.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 8;15:1483595. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1483595. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39439806 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
- 113-G6-1-2/VGHUST Joint Research Program
- 113-G6-1-2/VGHUST Joint Research Program
- VGHKS113-061 and 113-092/Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital
- NTSC 112-2314-B-075-B-008 and 112-2314-B-442-001/National Science and Technology Council
- NTSC 112-2314-B-075-B-008 and 112-2314-B-442-001/National Science and Technology Council
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

