Prevalence of autoimmune thyroiditis among children with autoimmune hepatitis
- PMID: 38632644
- PMCID: PMC11025222
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-024-01639-4
Prevalence of autoimmune thyroiditis among children with autoimmune hepatitis
Abstract
Background: Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is an organ specific autoimmune disease, which can manifest at any age of life. there is a high prevalence of extrahepatic autoimmune diseases in patients with AIH. Autoimmune thyroid diseases (ATDs) are the most frequent extrahepatic autoimmune disorders among patients with AIH. Aim of work is to detect the frequency of ATDs among Egyptian children with AIH.
Methods: This research is a cross-sectional study conducted on 58 children with AIH aged ≤ 18 years. All patients were tested for free triiodothyronine (FT3), free tetraiodothyronine (FT4), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) and antithyroglobulin (anti-TG). Thyroid ultrasound (US) and thyroid scan were performed for patients with abnormal thyroid profile, borderline values, positive anti-TPO or anti-TG.
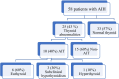
Results: The mean ± standard deviation (SD) for the age of the patients was 11.3 ± 4.5 years. Out of 58 patients of AIH, 28 patients (48.3%) had associated other autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune thyroiditis was the most common associated autoimmune disease being present in 10 patients (17.2%). The thyroid status of AIT patients showed that 6 patients (60%) were euthyroid, 3 patients (30%) had subclinical hypothyroidism and only one patient (10%) was hyperthyroid.
Conclusion: Autoimmune hepatitis in Egyptian children is commonly associated with other autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune thyroiditis is the most common to be associated with AIH in pediatric patients. As it is not usually clinically manifesting, regular screening for AIT in children with AIH is mandatory.
Keywords: Autoimmune diseases; Autoimmune hepatitis; Autoimmune thyroiditis; Children.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polycystic ovary syndrome and chronic autoimmune thyroiditis.Gynecol Endocrinol. 2015 Jan;31(1):48-51. doi: 10.3109/09513590.2014.958990. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25211537
-
Impact of nutritional iodine optimization on rates of thyroid hypoechogenicity and autoimmune thyroiditis: a cross-sectional, comparative study.Thyroid. 2015 Jan;25(1):118-24. doi: 10.1089/thy.2014.0182. Thyroid. 2015. PMID: 25314342
-
Prevalence of interrelated autoantibodies in thyroid diseases and autoimmune disorders.J Endocrinol Invest. 2008 Oct;31(10):861-5. doi: 10.1007/BF03346432. J Endocrinol Invest. 2008. PMID: 19092289
-
Myoinositol in Autoimmune Thyroiditis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 28;13:930756. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.930756. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35837308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Autoimmune thyroiditis: diagnosis and treatment].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2009 Dec;134(49):2504-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1243053. Epub 2009 Nov 25. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2009. PMID: 19941232 Review. German.
References
-
- Khoury T, et al. Thyroid dysfunction is prevalent in autoimmune hepatitis: a case control study. Isr Med Assoc J. 2020;22(2):100–103. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous