Klotho-mediated activation of the anti-oxidant Nrf2/ARE signal pathway affects cell apoptosis, senescence and mobility in hypoxic human trophoblasts: involvement of Klotho in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia
- PMID: 38632651
- PMCID: PMC11025225
- DOI: 10.1186/s13008-024-00120-2
Klotho-mediated activation of the anti-oxidant Nrf2/ARE signal pathway affects cell apoptosis, senescence and mobility in hypoxic human trophoblasts: involvement of Klotho in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia
Abstract
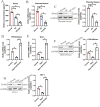
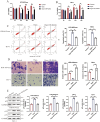
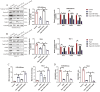
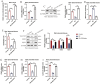
The anti-aging gene Klotho is implicated in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia (PE), which is a pregnancy disease characterized by hypertension and proteinuria. Oxidative stress is closely associated with the worse outcomes in PE, and Klotho can eliminate Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), but it is still unclear whether Klotho regulates PE pathogenesis through modulating oxidative damages. Here, by analyzing the clinical data, we found that Klotho was aberrantly downregulated in PE umbilical cord serum and placental tissues, compared to their normal counterparts. In in vitro experiments, the human trophoblasts were subjected to hypoxic pressure to establish the PE models, and we confirmed that hypoxia also decreased the expression levels of Klotho in those trophoblasts. In addition, through performing functional experiments, we confirmed that hypoxia promoted oxidative damages, cell apoptosis and senescence, whereas suppressed cell invasion in human trophoblasts, which were all reversed overexpressing Klotho. The following mechanical experiments verified that Klotho increased the levels of nuclear Nrf2, total Nrf2, SOD2 and NQO1 to activate the anti-oxidant Nrf2/ARE signal pathway, and silencing of Nrf2 abrogated the protective effects of Klotho overexpression on hypoxic human trophoblasts. Consistently, in in vivo experiments, Klotho overexpression restrained oxidative damages and facilitated cell mitosis in PE rats' placental tissues. In conclusion, this study validated that Klotho activated the Nrf2/ARE signal pathway to eliminate hypoxia-induced oxidative damages, cell apoptosis and senescence to recover normal cellular functions in human trophoblasts, and our data supported that Klotho could be used as novel biomarker for PE diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: Human trophoblasts; Hypoxia; Nrf2/ARE signal pathway; Oxidative stress; Preeclampsia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Klotho ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by activating Nrf2 signaling pathway in podocytes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jan 1;534:450-456. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.061. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33256980
-
MiR-133b regulates oxidative stress injury of trophoblasts in preeclampsia by mediating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.J Mol Histol. 2021 Dec;52(6):1177-1188. doi: 10.1007/s10735-021-10024-y. Epub 2021 Oct 8. J Mol Histol. 2021. PMID: 34623553
-
LINC00240/miR-155 axis regulates function of trophoblasts and M2 macrophage polarization via modulating oxidative stress-induced pyroptosis in preeclampsia.Mol Med. 2022 Sep 24;28(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00531-3. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36153499 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylcholine ameliorated hypoxia-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in trophoblast cells via p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway.Mol Hum Reprod. 2021 Aug 7;27(8):gaab045. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaab045. Mol Hum Reprod. 2021. PMID: 34245298
-
Modulation of NRF2/KEAP1 Signaling in Preeclampsia.Cells. 2023 Jun 4;12(11):1545. doi: 10.3390/cells12111545. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37296665 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between pan-immune-inflammation value and Serum Klotho levels: a cross-sectional analysis of renal function mediation.Front Immunol. 2025 May 30;16:1567367. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1567367. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40519908 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin Attenuates PFOS-Induced Reproductive Toxicity of Pregnant Mice due to Placental Damage Via Antioxidant, Anti-Aging and Anti-Inflammatory Pathways.Birth Defects Res. 2024 Dec;116(12):e2423. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.2423. Birth Defects Res. 2024. PMID: 39665241 Free PMC article.
-
Preeclampsia as a Study Model for Aging: The Klotho Gene Paradigm.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 22;26(3):902. doi: 10.3390/ijms26030902. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940672 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang Y, Liu W, Zhong Y, Li Q, Wu M, Yang L, Liu X, Zou L. Metformin corrects glucose metabolism reprogramming and NLRP3 inflammasome-induced pyroptosis via inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB/PFKFB3 signaling in trophoblasts: implication for a potential therapy of preeclampsia. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:1806344. doi: 10.1155/2021/1806344. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

