Exploring the Design of Upper Limb Strength Training Through High-Intensity Interval Training Combined With Exergaming: Usability Study
- PMID: 38632713
- PMCID: PMC11040163
- DOI: 10.2196/51730
Exploring the Design of Upper Limb Strength Training Through High-Intensity Interval Training Combined With Exergaming: Usability Study
Abstract
Background: High-intensity interval training (HIIT) has become a popular exercise strategy in modern society, with the Tabata training method being the most popular. In the past, these training methods were mostly done without equipment, but incorporating exergaming into the training may provide a new option for muscle training.
objectives: The aim of this study was to explore the differences in upper limb muscle activation using an HIIT program combined with exergaming.
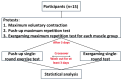
Methods: A total of 15 healthy male participants were recruited for the study, and the differences in muscle activation were compared between push-ups and exergaming (Nintendo Switch Ring Fit Adventure with the Ring-Con accessory) during HIIT. Prior to the tests, participants underwent pretests, including maximal voluntary contractions of various muscle groups, maximal push-up tests, and maximal movement tests using the exergaming device. The push-up and exergaming tests were conducted on separate days to avoid interference, with a warm-up period of 5 minutes on a treadmill before testing. Muscle activation in the lateral and anterior portions of the deltoid muscle, the sternal and clavicular heads of the pectoralis major muscle, and the latissimus dorsi muscle were measured during the maximal voluntary contractions and single-round tests for each exercise mode. A repeated measures ANOVA was used to assess the variations in muscle activation observed across the 2 distinct modes of exercise, specifically push-ups and exergaming.
Results: In exergaming, the number of repetitions for push-ups was significantly fewer than for single-site exercises across both exhaustive (mean 23.13, SD 6.36 vs mean 55.67, SD 17.83; P=.001; effect size [ES]: 2.43) and single-round (mean 21.93, SD 7.67 vs mean 92.40, SD 20.47; P=.001; ES: 4.56) training. Heart rate differences were not significant (all P>.05), yet exergaming led to better muscle activation in specific muscle groups, particularly the right anterior deltoid (mean 48.00%, SD 7.66% vs mean 32.84%, SD 10.27%; P=.001; ES: 1.67) and right pectoralis major (sternal head: mean 38.99%, SD 9.98% vs mean 26.90%, SD 12.97%; P=.001; ES: 1.04; clavicular head: mean 43.54%, SD 9.59% vs mean 30.09%, SD 11.59%; P=.002; ES: 1.26) during exhaustive training. In single-round training, similar patterns were observed with the anterior deltoid (mean 51.37%, SD 11.76% vs mean 35.47%, SD 12.72%; P=.002; ES: 1.30) and pectoralis major (sternal head: mean 53.27%, SD 10.79% vs mean 31.56%, SD 16.92%; P=.001; ES: 1.53; clavicular head: mean 53.75%, SD 13.01% vs mean 37.95%, SD 14.67%; P=.006; ES: 1.14). These results suggest that exergaming may be more effective for targeted muscle activation.
Conclusions: In conclusion, HIIT can increase muscle activation in the upper extremities and can be incorporated into exergaming strategies to provide a fun and engaging way to exercise.
Keywords: electromyography; exercise; healthy; home training; muscle.
© Shu-Cheng Lin, Jing-Yu Lee, Yong Yang, Chu-Chun Fang, Hsiao-Lin Fang, Tien-Hung Hou. Originally published in JMIR Serious Games (https://games.jmir.org).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Erratum.Mult Scler. 2016 Oct;22(12):NP9-NP11. doi: 10.1177/1352458515585718. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Mult Scler. 2016. PMID: 26041800
-
Impact of Fruit and Vegetable Enzyme Supplementation on Aerobic Performance and Lactate Response in Older Adults Following High-Intensity Interval Exercise Through Exergaming: Randomized Experimental Matched-Pair Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2024 Jun 25;12:e52231. doi: 10.2196/52231. JMIR Serious Games. 2024. PMID: 38967387 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of Shoulder Prime Movers and Torso Stabilizers During Push-Up Exercises Using a Suspension Training System.J Sport Rehabil. 2020 Jan 7;29(7):993-1000. doi: 10.1123/jsr.2019-0381. Print 2020 Sep 1. J Sport Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 31910394
-
Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training in School on the Physical Performance and Health of Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.Sports Med Open. 2022 Apr 11;8(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s40798-022-00437-8. Sports Med Open. 2022. PMID: 35403996 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual-reality exergaming improves performance during high-intensity interval training.Eur J Sport Sci. 2019 Jul;19(6):719-727. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2018.1542459. Epub 2018 Nov 7. Eur J Sport Sci. 2019. PMID: 30403927 Review.
Cited by
-
Playful Antisedentary Interactions for Online Meeting Scenarios: A Research Through Design Approach.JMIR Serious Games. 2025 Apr 18;13:e62778. doi: 10.2196/62778. JMIR Serious Games. 2025. PMID: 40249120 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

