Anti-neuraminidase immunity in the combat against influenza
- PMID: 38632930
- PMCID: PMC11157429
- DOI: 10.1080/14760584.2024.2343689
Anti-neuraminidase immunity in the combat against influenza
Abstract
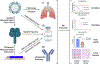
Introduction: Anti-neuraminidase (NA) immunity correlates with the protection against influenza virus infection in both human and animal models. The aim of this review is to better understand the mechanism of anti-NA immunity, and also to evaluate the approaches on developing NA-based influenza vaccines or enhancing immune responses against NA for current influenza vaccines.
Areas covered: In this review, the structure of influenza neuraminidase, the contribution of anti-NA immunity to protection, as well as the efforts and challenges of targeting the immune responses to NA were discussed. We also listed some of the newly discovered anti-NA monoclonal antibodies and discussed their contribution in therapeutic as well as the antigen design of a broadly protective NA vaccine.
Expert opinion: Targeting the immune response to both HA and NA may be critical for achieving the optimal protection since there are different mechanisms of HA and NA elicited protective immunity. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that target the conserved protective lateral face or catalytic sites are effective therapeutics. The epitope discovery using monoclonal antibodies may benefit NA-based vaccine elicited broadly reactive antibody responses. Therefore, the potential for a vaccine that elicits cross-reactive antibodies against neuraminidase is a high priority for next-generation influenza vaccines.
Keywords: Influenza; anti-NA immunity; antibodies; hemagglutinin; neuraminidase; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants, patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures
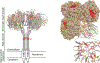
References
-
- Jiang L, Changsom D, Lerdsamran H, et al. Cross-reactive antibodies against H7N9 and H5N1 avian influenza viruses in Thai population. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2017. Mar;35(1):20–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
