Melanin-like nanoparticles alleviate ischemia-reperfusion injury in the kidney by scavenging reactive oxygen species and inhibiting ferroptosis
- PMID: 38632989
- PMCID: PMC11022057
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109504
Melanin-like nanoparticles alleviate ischemia-reperfusion injury in the kidney by scavenging reactive oxygen species and inhibiting ferroptosis
Abstract
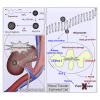
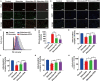
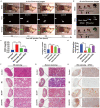
Kidney transplantation is essential for patients with end-stage renal disease; however, ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) during transplantation can lead to acute kidney damage and compromise survival. Recent studies have reported that antiferroptotic agents may be a potential therapeutic strategy, by reducing production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Therefore, we constructed rutin-loaded polydopamine nanoparticles (PEG-PDA@rutin NPs, referred to as PPR NPs) to eliminate ROS resulting from IRI. Physicochemical characterization showed that the PPR NPs were ∼100 nm spherical particles with good ROS scavenging ability. Notably, PPR NPs could effectively enter lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated renal tubular cells, then polydopamine (PDA) released rutin to eliminate ROS, repair mitochondria, and suppress ferroptosis. Furthermore, in vivo imaging revealed that PPR NPs efficiently accumulated in the kidneys after IRI and effectively protected against IRI damage. In conclusion, PPR NPs demonstrated an excellent ability to eliminate ROS, suppress ferroptosis, and protect kidneys from IRI.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Biomedical materials; Drug delivery system; Nanoparticles.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel gold-platinum nanoparticles serve as broad-spectrum antioxidants for attenuating ischemia reperfusion injury of the kidney.Kidney Int. 2022 Nov;102(5):1057-1072. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.004. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Kidney Int. 2022. PMID: 35870640
-
Ultra-Small Copper-Based Multienzyme-Like Nanoparticles Protect Against Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through Scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species in Mice.Small. 2024 Dec;20(51):e2403313. doi: 10.1002/smll.202403313. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Small. 2024. PMID: 39377344
-
Prevention of Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Carbohydrate-Derived Nanoantioxidants.Nano Lett. 2020 Sep 9;20(9):6510-6519. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c02248. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Nano Lett. 2020. PMID: 32786929 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Responsive Nanomedicine for Solving Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Front Chem. 2020 Aug 21;8:732. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00732. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 32974285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting ferroptosis in ischemia/reperfusion renal injury.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Nov;395(11):1331-1341. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02277-5. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35920897 Review.
Cited by
-
Iron homeostasis and ferroptosis in human diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic prospects.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Oct 14;9(1):271. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01969-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39396974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological Roles of Eumelanin- and Melanogenesis-Associated Diseases: A Look at the Potentialities of Engineered and Microbial Eumelanin in Clinical Practice.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jul 25;11(8):756. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11080756. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress: Signaling Pathways, Biological Functions, and Disease.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jul 1;6(7):e70268. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70268. eCollection 2025 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40599237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of inflammatory response and metabolic reprogramming in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: mechanistic insights and therapeutic potential.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 31;15:1487576. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1487576. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39544947 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Minami K., Bae S., Uehara H., Zhao C., Lee D., Iske J., Fanger M.W., Reder J., Morrison I., Azuma H., et al. Targeting of intragraft reactive oxygen species by APP-103, a novel polymer product, mitigates ischemia/reperfusion injury and promotes the survival of renal transplants. Am. J. Transplant. 2020;20:1527–1537. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15794. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

