Optimizing early neurological deterioration prediction in acute ischemic stroke patients following intravenous thrombolysis: a LASSO regression model approach
- PMID: 38633265
- PMCID: PMC11022961
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1390117
Optimizing early neurological deterioration prediction in acute ischemic stroke patients following intravenous thrombolysis: a LASSO regression model approach
Abstract
Background: Acute ischemic stroke (AIS) remains a leading cause of disability and mortality globally among adults. Despite Intravenous Thrombolysis (IVT) with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) emerging as the standard treatment for AIS, approximately 6-40% of patients undergoing IVT experience Early Neurological Deterioration (END), significantly impacting treatment efficacy and patient prognosis.
Objective: This study aimed to develop and validate a predictive model for END in AIS patients post rt-PA administration using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression approach.
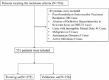
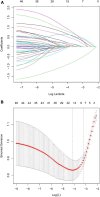
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, data from 531 AIS patients treated with intravenous alteplase across two hospitals were analyzed. LASSO regression was employed to identify significant predictors of END, leading to the construction of a multivariate predictive model.
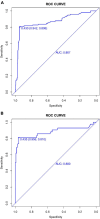
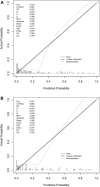
Results: Six key predictors significantly associated with END were identified through LASSO regression analysis: previous stroke history, Body Mass Index (BMI), age, Onset to Treatment Time (OTT), lymphocyte count, and glucose levels. A predictive nomogram incorporating these factors was developed, effectively estimating the probability of END post-IVT. The model demonstrated robust predictive performance, with an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.867 in the training set and 0.880 in the validation set.
Conclusion: The LASSO regression-based predictive model accurately identifies critical risk factors leading to END in AIS patients following IVT. This model facilitates timely identification of high-risk patients by clinicians, enabling more personalized treatment strategies and optimizing patient management and outcomes.
Keywords: LASSO regression; acute ischemic stroke (AIS); early neurological deterioration (END); intravenous thrombolysis (IVT); predictive modeling.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Li, Shao, Wang, Li and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A predictive model for early neurological deterioration after intravenous thrombolysis in patients with ischemic stroke.Front Neurol. 2025 Feb 17;16:1477286. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1477286. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40035033 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of serum MDA and 4-HNE levels on the occurrence of early neurological deterioration after intravenous thrombolysis with rt-PA IVT in patients with acute ischemic stroke.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024 Apr;33(4):107574. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2024.107574. Epub 2024 Jan 11. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38214238
-
Machine learning-based prediction of early neurological deterioration after intravenous thrombolysis for stroke: insights from a large multicenter study.Front Neurol. 2024 Sep 9;15:1408457. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1408457. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39314867 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian Rhythm and Risk of Hemorrhagic Transformation after Acute Ischemic Stroke Treated with Intravenous Thrombolysis - A Systematic Review.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2023;22(10):1493-1506. doi: 10.2174/1871527322666221004113752. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2023. PMID: 36200200
-
Predictors of Early Neurological Deterioration Occurring within 24 h in Acute Ischemic Stroke following Reperfusion Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Integr Neurosci. 2023 Mar 23;22(2):52. doi: 10.31083/j.jin2202052. J Integr Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36992598
Cited by
-
A machine learning-based predictive model for predicting early neurological deterioration in lenticulostriate atheromatous disease-related infarction.Front Neurosci. 2024 Dec 11;18:1496810. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1496810. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39723423 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a predictive model for poor long-term prognosis in severe acute ischemic stroke after endovascular treatment based on LASSO regression.Front Neurol. 2025 Apr 14;16:1535679. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1535679. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40297852 Free PMC article.
-
Atherogenic Dyslipidemia Is Critically Related to Aortic Complicated Lesions in Cryptogenic Stroke.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2025 Jul 1;32(7):804-822. doi: 10.5551/jat.65289. Epub 2024 Dec 26. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2025. PMID: 39721702 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Stroke Severity Assessment: The Impact of Lesion Size and Functional Connectivity.Brain Sci. 2025 Jul 9;15(7):735. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15070735. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40722326 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretable prediction of stroke prognosis: SHAP for SVM and nomogram for logistic regression.Front Neurol. 2025 Mar 4;16:1522868. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1522868. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40103937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrio I., Arostegui I., Rodrí-guez-Álvarez M., Quintana J. (2017). A new approach to categorising continuous variables in prediction models: Proposal and validation. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 26, 2586–2602. - PubMed
-
- Broccolini A., Brunetti V., Colò F., Alexandre A., Valente I., Falcou A., et al. (2023). Early neurological deterioration in patients with minor stroke due to isolated M2 occlusion undergoing medical management: A retrospective multicenter study. J. Neurointervent. Surg. 16 38–44. 10.1136/jnis-2023-020118 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

