Formulation and evaluation of azithromycin-loaded silver nanoparticles for the treatment of infected wounds
- PMID: 38633410
- PMCID: PMC11021372
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2024.100245
Formulation and evaluation of azithromycin-loaded silver nanoparticles for the treatment of infected wounds
Abstract
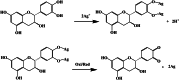
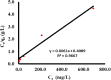
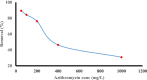
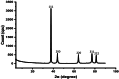
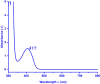
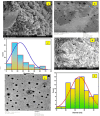
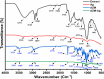
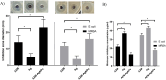
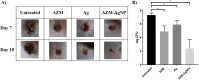
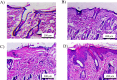
Infected wounds pose a significant challenge in healthcare, requiring innovative therapeutic strategies. Therefore, there is a critical need for innovative pharmaceutical materials to improve wound healing and combat bacterial growth. This study examined the efficacy of azithromycin-loaded silver nanoparticles (AZM-AgNPs) in treating infected wounds. AgNPs synthesized using a green method with Quinoa seed extract were loaded with AZM. Characterization techniques, including X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), and Uv-Vis analysis were utilized. The agar diffusion assay and determination of the MIC were used to assess the initial antibacterial impact of the formulations on both MRSA and E. coli. In addition, the antimicrobial, wound-healing effects and histological changes following treatment with the AZM-AgNPs were assessed using an infected rat model. The nanoparticles had size of 24.9 ± 15.2 nm for AgNPs and 34.7 ± 9.7 nm for AZM-AgNPs. The Langmuir model accurately characterized the adsorption of AZM onto the AgNP surface, indicating a maximum loading capacity of 162.73 mg/g. AZM-AgNPs exhibited superior antibacterial properties in vivo and in vitro compared to controls. Using the agar diffusion technique, AZM-AgNPs showed enhanced zones of inhibition against E. coli and MRSA, which was coupled with decreased MIC levels. In addition, in vivo studies showed that AZM-AgNP treated rats had the best outcome characterized by improved healing process, lower bacterial counts and superior epithelialization, compared to the control group. In conclusion, AZM-AgNPs can be synthesized using a green method with Quinoa seed with successful loading of azithromycin onto silver nanoparticles. In vitro and in vivo studies suggest the promising use of AZM-AgNPs as an effective therapeutic agent for infected wounds.
Keywords: AZM-AgNPs; Adsorption isotherm; Green biosynthesis; Infected wound.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tailoring of Novel Azithromycin-Loaded Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Wound Healing.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jan 5;14(1):111. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010111. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35057019 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesis and Evaluation of Lepidium didymum-mediated Silver Nanoparticles for in vitro Antibacterial Activity and Wound Healing in the Animal Model.J Oleo Sci. 2023 Mar 30;72(4):429-439. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess22380. Epub 2023 Mar 10. J Oleo Sci. 2023. PMID: 36908177
-
Characterization, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Aqueous Extracts of Allium sativum, Zingiber officinale, and Capsicum frutescens.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jul;13(Suppl 2):S201-S208. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_430_16. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 28808381 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Evaluation of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles-Kaempferol for Antibacterial Activity Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Feb 8;19:1339-1350. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S431499. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38348172 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Loaded Hydrogel for Wound Healing; Systematic Review.Gels. 2023 Jun 29;9(7):530. doi: 10.3390/gels9070530. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37504410 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advancing biomedical applications: an in-depth analysis of silver nanoparticles in antimicrobial, anticancer, and wound healing roles.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 8;15:1438227. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1438227. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39175537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fabrication of novel vildagliptin loaded ZnO nanoparticles for anti diabetic activity.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 2;14(1):17893. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67420-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39095369 Free PMC article.
-
HPMC-Zein Film-forming Gel Loaded with 5-Fluorouracil Coupled with CO2 Laser Dermabrasion for Managing Stable Vitiligo.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Sep 26;25(7):225. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02937-0. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 39327349
-
Enhanced urease inhibitory activity of quercetin via conjugation with silver nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and DFT study.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 7;15(1):11892. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96684-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40195446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbasifar A., Ghani S., Irvani M.A., Rafiee B., Kaji B.V., Akbari A. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized by using extracts of Hedera helix. Zahedan J. Res.Med. Sci. 2017:19.
-
- Abdullah M., Iqbal J., Ur Rehman M.S., Khalid U., Mateen F., Arshad S.N., Al-Sehemi A.G., Algarni H., Al-Hartomy O.A., Fazal T. Removal of ceftriaxone sodium antibiotic from pharmaceutical wastewater using an activated carbon based TiO2 composite: Adsorption and photocatalytic degradation evaluation. Chemosphere. 2023;317:137834. - PubMed
-
- Abu-Dief A.M., Abdel-Rahman L.H., Abd-El Sayed M.A., Zikry M.M., Nafady A. Green synthesis of AgNPs ultilizing Delonix Regia extract as anticancer and antimicrobial agents. ChemistrySelect. 2020;5(42):13263–13268.
-
- Abu-Dief A.M., Abdel-Rahman L.H., Sayed M.A.E., Zikry M.M., Khalifa M.E., El-Metwaly N.M. Optimization strategy for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) as catalyst for the reduction of 2, 4-dinitrophenol via supported mechanism. Appl. Phys. A. 2022;128(7):595.
-
- Ahmadi S. The importance of silver nanoparticles in human life. Adv. Appl. NanoBio-Technol. 2020;1:5–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

