Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: a key mechanism in the occurrence and development of cancer
- PMID: 38634043
- PMCID: PMC11021590
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1381467
Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: a key mechanism in the occurrence and development of cancer
Abstract
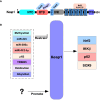
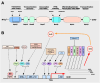
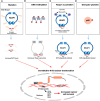
The Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway is a major regulator of the cytoprotective response, participating in endogenous and exogenous stress caused by ROS (reactive oxygen species). Nrf2 is the core of this pathway. We summarized the literature on Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway and summarized the following three aspects: structure, function pathway, and cancer and clinical application status. This signaling pathway is similar to a double-edged sword: on the one hand, Nrf2 activity can protect cells from oxidative and electrophilic stress; on the other hand, increasing Nrf2 activity can enhance the survival and proliferation of cancer cells. Notably, oxidative stress is also considered a marker of cancer in humans. Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway, as a typical antioxidant stress pathway, is abnormal in a variety of human malignant tumor diseases (such as lung cancer, liver cancer, and thyroid cancer). In recent years, research on the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway has become increasingly in-depth and detailed. Therefore, it is of great significance for cancer prevention and treatment to explore the molecular mechanism of the occurrence and development of this pathway.
Keywords: Keap1; Nrf2; cancer; clinical; function; prevention; structure; transcriptional regulation.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Xiao, Hu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: promising therapeutic target to counteract ROS-mediated damage in cancers and neurodegenerative diseases.Biophys Rev. 2017 Feb;9(1):41-56. doi: 10.1007/s12551-016-0244-4. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Biophys Rev. 2017. PMID: 28510041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf2 Modulation in Breast Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 21;10(10):2668. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102668. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Nrf2/HO-1 by Natural Compounds in Lung Cancer.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Mar 16;12(3):735. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030735. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ameliorative inhibition of sirtuin 6 by imidazole derivative triggers oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis associated with Nrf2/Keap1 signaling in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 3;14:1335305. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1335305. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38235110 Free PMC article.
-
MDA-7/IL-24 inhibits Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response through activation of p38 pathway and inhibition of ERK pathway involved in cancer cell apoptosis.Cancer Gene Ther. 2014 Oct;21(10):416-26. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2014.45. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Cancer Gene Ther. 2014. PMID: 25236495
Cited by
-
Exploring Chemoprevention in Colorectal Cancer for Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Aspects.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 12;17(2):229. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020229. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulforaphane attenuates phosgene-induced acute lung injury via the Nrf2-HO-1/NQO1 pathway.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Oct 31;16(10):6604-6615. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-819. Epub 2024 Oct 30. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 39552873 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin induces oxidative stress and apoptosis via dysregulating the cytoprotective Nrf2-Keap1-Cul3 redox signaling in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Dec 19;52(1):65. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10178-4. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39699825
-
Effects of Lysophospholipids on the Antioxidant Capacity, Digestive Performance, and Intestinal Microbiota of Litopenaeus vannamei.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jan 17;14(1):90. doi: 10.3390/biology14010090. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857320 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis: CD8+T cells' blade to destroy tumor cells or poison for self-destruction.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Apr 1;11(1):128. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02415-x. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40169575 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

