Comparative efficacy and safety of targeted therapy and immunotherapy for HER2-positive breast cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analyses
- PMID: 38634057
- PMCID: PMC11021689
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1331055
Comparative efficacy and safety of targeted therapy and immunotherapy for HER2-positive breast cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analyses
Abstract
Background: In recent years, novel therapies targeting specific molecular pathways and immunotherapies have exhibited promising outcomes for treating human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer. Our work aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of these emerging treatment regimens for this disease.
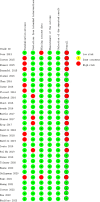
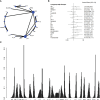
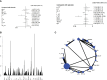
Material and methods: We systematically searched databases including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials their inception to August 2023 to identify relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The quality of eligible RCTs was evaluated with the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool, version 2 (RoB2). Investigated outcomes encompassed progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), pathologic complete remission (pCR), and adverse events (AEs). They were expressed as hazard ratio (HR) with 95% conference intervals (CI) or risk ratio (RR) with 95% CI.
Results: Our analysis identified a total of 28 RCTs suitable for inclusion in the NMA. Regarding the PFS, all these treatment regimens exhibited comparable effectiveness. In terms of OS, Capecitabine+Trastuzumab, Lapatinib+Trastuzumab and Pyrotinib+Capecitabine exhibited better effect compared to other treatments. Regarding pCR and AEs, all these treatment regimens exhibited comparable effectiveness, especially Lapatinib+Trastuzumab and Pyrotinib+Capecitabine.
Conclusion: Our study highlights the prominent role of targeted therapies and immunotherapies in treating HER2-positive breast cancer. The efficacy of trastuzumab-containing regimens was superior to other treatment options, while maintaining a comparable safety profile. Based on these findings, trastuzumab-containing regimens emerge as a preferable and recommended choice in clinical practice for managing HER2-positive breast cancer.
Systematic review registration: PROSPERO, identifier CRD42023414348.
Keywords: HER2-positive; breast cancer; efficacy; immunotherapies; meta-analysis; safety.
Copyright © 2024 Gu, Liu, Huang, Lin and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HER2-targeted regimens after prior trastuzumab for patients with HER2-positive unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Dec;8(24):1634. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-5149. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33490146 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrotinib versus lapatinib therapy for HER2 positive metastatic breast cancer patients after first-line treatment failure: A meta-analysis and systematic review.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 5;18(1):e0279775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279775. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36602979 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of second-line treatments for patients with advanced human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer after trastuzumab-based treatment: a systematic review and bayesian network analysis.J Cancer. 2021 Jan 18;12(6):1687-1697. doi: 10.7150/jca.51845. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33613756 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Pyrotinib Versus T-DM1 in HER2+ Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Pre-Treated With Trastuzumab and a Taxane: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 May 3;11:608781. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.608781. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34012912 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of tucatinib for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer after HER2-targeted therapy: a network meta-analysis.Future Oncol. 2021 Nov;17(33):4635-4647. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-0742. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Future Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34463120
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

