Combination of high anti-SKI and low anti-TMED5 antibody levels is preferable prognostic factor in esophageal carcinoma
- PMID: 38634426
- PMCID: PMC11247554
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.16185
Combination of high anti-SKI and low anti-TMED5 antibody levels is preferable prognostic factor in esophageal carcinoma
Abstract
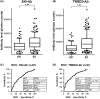
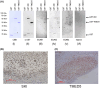
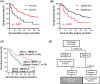
Given that esophageal cancer is highly malignant, the discovery of novel prognostic markers is eagerly awaited. We performed serological identification of antigens by recombinant cDNA expression cloning (SEREX) and identified SKI proto-oncogene protein and transmembrane p24 trafficking protein 5 (TMED5) as antigens recognized by serum IgG antibodies in patients with esophageal carcinoma. SKI and TMED5 proteins were expressed in Escherichia coli, purified by affinity chromatography, and used as antigens. The serum anti-SKI antibody (s-SKI-Ab) and anti-TMED5 antibody (s-TMED5-Ab) levels were significantly higher in 192 patients with esophageal carcinoma than in 96 healthy donors. The presence of s-SKI-Abs and s-TMED5-Abs in the patients' sera was confirmed by western blotting. Immunohistochemical staining showed that the TMED5 protein was highly expressed in the cytoplasm and nuclear compartments of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues, whereas the SKI protein was localized predominantly in the nuclei. Regarding the overall survival in 91 patients who underwent radical surgery, the s-SKI-Ab-positive and s-TMED5-Ab-negative statuses were significantly associated with a favorable prognosis. Additionally, the combination of s-SKI-Ab-positive and s-TMED5-Ab-negative cases showed an even clearer difference in overall survival as compared with that of s-SKI-Ab-negative and s-TMED5-Ab-positive cases. The s-SKI-Ab and s-TMED5-Ab biomarkers are useful for diagnosing esophageal carcinoma and distinguishing between favorable and poor prognoses.
Keywords: SKI; TMED5; antibody biomarker; esophageal carcinoma; overall survival.
© 2024 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Hideaki Shimada is an editorial board member of
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of anti-CUEC-23 antibodies in serum of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a possible new serum marker for esophageal cancer.J Gastroenterol. 2009;44(7):691-6. doi: 10.1007/s00535-009-0060-8. Epub 2009 May 1. J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19407926
-
Anti-FIRΔexon2, a splicing variant form of PUF60, autoantibody is detected in the sera of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2019 Jun;110(6):2004-2013. doi: 10.1111/cas.14024. Epub 2019 May 20. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30980774 Free PMC article.
-
Low anti-CFL1 antibody with high anti-ACTB antibody is a poor prognostic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Esophagus. 2022 Oct;19(4):617-625. doi: 10.1007/s10388-022-00939-0. Epub 2022 Jul 3. Esophagus. 2022. PMID: 35780443
-
Presence of serum tripartite motif-containing 21 antibodies in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2006 May;97(5):380-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00192.x. Cancer Sci. 2006. PMID: 16630135 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Serum Anti-PCSK9 Antibody Levels with Favorable Postoperative Prognosis in Esophageal Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 24;11:708039. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.708039. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34504788 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Application of serum anti-ENO1 and anti-SSNA1 antibody biomarkers in predicting the prognosis of gastric cancer.Oncol Lett. 2025 May 22;30(1):360. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.15106. eCollection 2025 Jul. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40469915 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

