Bioinformatics analysis of the potentially functional circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in breast cancer
- PMID: 38635539
- PMCID: PMC11025867
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301995
Bioinformatics analysis of the potentially functional circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in breast cancer
Abstract
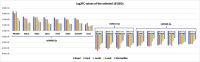
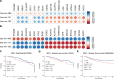
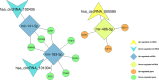
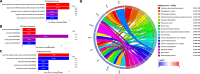
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer among women with high morbidity and mortality. Therefore, new research is still needed for biomarker detection. GSE101124 and GSE182471 datasets were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database to evaluate differentially expressed circular RNAs (circRNAs). The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Molecular Taxonomy of Breast Cancer International Consortium (METABRIC) databases were used to identify the significantly dysregulated microRNAs (miRNAs) and genes considering the Prediction Analysis of Microarray classification (PAM50). The circRNA-miRNA-mRNA relationship was investigated using the Cancer-Specific CircRNA, miRDB, miRTarBase, and miRWalk databases. The circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network was annotated using Gene Ontology (GO) analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway database. The protein-protein interaction network was constructed by the STRING database and visualized by the Cytoscape tool. Then, raw miRNA data and genes were filtered using some selection criteria according to a specific expression level in PAM50 subgroups. A bottleneck method was utilized to obtain highly interacted hub genes using cytoHubba Cytoscape plugin. The Disease-Free Survival and Overall Survival analysis were performed for these hub genes, which are detected within the miRNA and circRNA axis in our study. We identified three circRNAs, three miRNAs, and eighteen candidate target genes that may play an important role in BC. In addition, it has been determined that these molecules can be useful in the classification of BC, especially in determining the basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) subtype. We conclude that hsa_circ_0000515/miR-486-5p/SDC1 axis may be an important biomarker candidate in distinguishing patients in the BLBC subgroup of BC.
Copyright: © 2024 Erdogan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Construction of a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network based on differentially co-expressed circular RNA in gastric cancer tissue and plasma by bioinformatics analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Feb 14;20(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02503-7. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35164778 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of endogenous RNA regulatory network for colorectal cancer based on bioinformatics.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Apr 28;47(4):416-430. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210532. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 35545337 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Identification of potentially functional circular RNAs hsa_circ_0070934 and hsa_circ_0004315 as prognostic factors of hepatocellular carcinoma by integrated bioinformatics analysis.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 23;12(1):4933. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08867-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35322101 Free PMC article.
-
Spotlight on Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs in Breast Cancer: An In Silico Analysis to Identify Potential lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-Target Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 28;23(15):8351. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158351. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico analysis and comprehensive review of circular-RNA regulatory roles in breast diseases; a step-toward non-coding RNA precision.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Nov;263:155651. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155651. Epub 2024 Oct 19. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39454476 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Role of hsa_circ_0052112 as a Potential Biomarker in Breast Cancer: Insights from Experimental and In Silico Analyses.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2025 Apr-Jun;17(2):136-146. doi: 10.18502/ajmb.v17i2.18565. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40453910 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of integrated ChIP-seq and transcriptome data revealed genomic regions affected by estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Sep 15;16(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01655-z. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37715225 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic dysregulation in cancer: mechanisms, diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic strategies.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 21;42(8):359. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02905-z. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40691387 Review.
-
Let-7b-5p sensitizes breast cancer cells to doxorubicin through Aurora Kinase B.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 9;20(1):e0307420. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307420. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39787178 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

