Microglia-derived extracellular vesicles trigger age-related neurodegeneration upon DNA damage
- PMID: 38635632
- PMCID: PMC11047102
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2317402121
Microglia-derived extracellular vesicles trigger age-related neurodegeneration upon DNA damage
Abstract
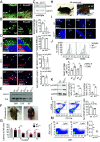
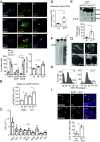
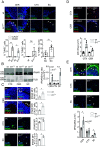
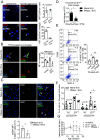
DNA damage and neurodegenerative disorders are intimately linked but the underlying mechanism remains elusive. Here, we show that persistent DNA lesions in tissue-resident macrophages carrying an XPF-ERCC1 DNA repair defect trigger neuroinflammation and neuronal cell death in mice. We find that microglia accumulate dsDNAs and chromatin fragments in the cytosol, which are sensed thereby stimulating a viral-like immune response in Er1Cx/- and naturally aged murine brain. Cytosolic DNAs are packaged into extracellular vesicles (EVs) that are released from microglia and discharge their dsDNA cargo into IFN-responsive neurons triggering cell death. To remove cytosolic dsDNAs and prevent inflammation, we developed targeting EVs to deliver recombinant DNase I to Er1Cx/- brain microglia in vivo. We show that EV-mediated elimination of cytosolic dsDNAs is sufficient to prevent neuroinflammation, reduce neuronal apoptosis, and delay the onset of neurodegenerative symptoms in Er1Cx/- mice. Together, our findings unveil a causal mechanism leading to neuroinflammation and provide a rationalized therapeutic strategy against age-related neurodegeneration.
Keywords: DNA damage; extracellular vesicles; microglia; neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adamec E., Vonsattel J. P., Nixon R. A., DNA strand breaks in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 849, 67–77 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Nunomura A., et al. , Oxidative damage is the earliest event in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 60, 759–767 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Alam Z. I., et al. , Oxidative DNA damage in the parkinsonian brain: An apparent selective increase in 8-hydroxyguanine levels in substantia nigra. J. Neurochem. 69, 1196–1203 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Bogdanov M., et al. , Increased oxidative damage to DNA in ALS patients. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 29, 652–658 (2000). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

