Real-world and clinical trial outcomes in large B-cell lymphoma with axicabtagene ciloleucel across race and ethnicity
- PMID: 38635762
- PMCID: PMC11251200
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2023023447
Real-world and clinical trial outcomes in large B-cell lymphoma with axicabtagene ciloleucel across race and ethnicity
Abstract
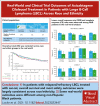
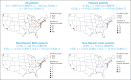
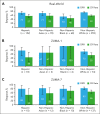
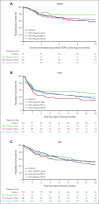
Axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) is an autologous anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy approved for relapsed/refractory (R/R) large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL). Despite extensive data supporting its use, outcomes stratified by race and ethnicity groups are limited. Here, we report clinical outcomes with axi-cel in patients with R/R LBCL by race and ethnicity in both real-world and clinical trial settings. In the real-world setting, 1290 patients who received axi-cel between 2017 and 2020 were identified from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research database; 106 and 169 patients were included from the ZUMA-1 and ZUMA-7 trials, respectively. Overall survival was consistent across race/ethnicity groups. However, non-Hispanic (NH) Black patients had lower overall response rate (OR, 0.37; 95% CI, 0.22-0.63) and lower complete response rate (OR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.33-0.97) than NH White patients. NH Black patients also had a shorter progression-free survival vs NH White (HR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.04-1.90) and NH Asian patients (HR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.08-2.59). NH Asian patients had a longer duration of response than NH White (HR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.33-0.94) and Hispanic patients (HR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.30-0.97). There was no difference in cytokine release syndrome by race/ethnicity; however, higher rates of any-grade immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome were observed in NH White patients than in other patients. These results provide important context when treating patients with R/R LBCL with CAR T-cell therapy across different racial and ethnic groups. ZUMA-1 and ZUMA-7 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifiers: #NCT02348216 and #NCT03391466, respectively) are registered on ClinicalTrials.gov.
© 2024 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: F.L.L. reports a scientific advisory role/consulting role with A2, Allogene, Amgen, bluebird bio, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Calibr, Caribou, Cellular Biomedicine Group, Cowen, Daiichi Sankyo, EcoR1, Emerging Therapy Solutions, GammaDelta Therapeutics, Gerson Lehrman Group, Iovance, Kite Pharma, Janssen, Legend Biotech, Novartis, Sana, Takeda, Wugen, and Umoja; reports patents, royalties, and other intellectual property in several patents held by the institution in his name (unlicensed) in the field of cellular immunotherapy; reports travel support from A2 Bio; and reports other relationships with Allogene (institutional), Aptitude Health, American Society of Hematology, bluebird bio (institutional), BioPharma Communications CARE Education, Bristol Myers Squibb (institutional), CERo Therapeutics (institutional), Clinical Care Options Oncology, Imedex, Kite (a Gilead company; institutional), Novartis (institutional), National Cancer Institute, Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, and Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer. T.S. held a consultancy or advisory role with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Celgene, Juno, and Kite (a Gilead company), and Pharmacyclics; reports speakers' bureau participation for AstraZeneca, BeiGene, and Bristol Myers Squibb; and reports institutional research funding from Ascentage Pharma, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Juno, Kite (a Gilead company), Oncternal, Pharmacyclics, and TG Therapeutics. C.A.J. held a consulting/advisory role with AbbVie, Abintus Bio, ADC Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Caribou Bio, Daiichi Sankyo, ImmPACT Bio, Instil Bio, Ipsen, Kite (a Gilead company), Miltenyi Biotec, MorphoSys, Novartis, and Synthekine; and reports research funding from Kite (a Gilead company) and Pfizer. A.G. received honoraria from Kite (a Gilead company); served in a consulting/advisory role for Amgen, Atara, Bristol Myers Squibb, CRISPR Therapeutics, Kite, and Wugen Inc; and reports research funding from Amgen, Genentech, and Kite. S.A. received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, Nektar, Tessa Therapeutics, and Xencor. D.B.M. received honoraria and travel support from Janssen; reports a consulting/advisory role for Adaptive Biotechnologies, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Kite (a Gilead company), and Miltenyi Biotec; reports research funding from 2Seventy Bio, Adicet, Allogene, Fate Therapeutics, Kite, and Miltenyi Biotec; and reports patents, royalties, or other intellectual property from chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) patent holder for ibrutinib as cGVHD therapy but no compensation. M.-A.P. received honoraria from AbbVie, Astellas, Celgene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, Karyopharm, Kite (a Gilead company), Miltenyi Biotec, MorphoSys, Novartis, Nektar Therapeutics, and Takeda; served in a consulting/advisory role for Merck and Omeros; reports institutional research funding for clinical trials from Incyte, Kite, Miltenyi Biotec, and Novartis; and reports other relationship with a Data Safety Monitoring Board: Cidara Therapeutics, Medigene, and Servier. J.M. received honoraria from Curio, Kyowa Kirin, OncView, Physicians' Education Resource, Targeted Oncology, and Seagen; reports consulting/advisory role for ADC Therapeutics, Alexion, Bayer, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Debiopharm, Epizyme, Fosunkite, Genmab, Innovent, Janssen, Juno/Celgene, Karyopharm, Kite (a Gilead company), Kyowa Kirin, Lilly/Loxo, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys/Incyte, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics/AbbVie, Seagen, Servier, TG Therapeutics, and Zodiac; reports speakers’ bureau participation for Acrotech/Aurobindo, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeiGene, Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech/Roche, Kite (a Gilead company), Kyowa Kirin, Pharmacyclics/Janssen, Seagen, and Verastem; and reports research funding from Bayer, Celgene, Genentech, Incyte, Janssen, Kite, Merck, Millennium, Pharmacyclics, Portola, and Seagen. M.P. reports honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb; served in a consulting/advisory role for Nektar Therapeutics; and declares travel support from Novartis. J.G. had a consulting/advisory role with Janssen, Kite (a Gilead company), Legend Biotech, MorphoSys, and Sobi; and received research funding from Angiocrine Bioscience, Celgene, Juno Therapeutics (a Bristol Myers Squibb company), and Sobi. M.S. had employment with Bristol Myers Squibb (spouse); served in a consulting/advisory role for AbbVie, Adaptimmune, Adaptive Biotechnologies, AstraZeneca, Atara Biotherapeutic, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Epizyme, Fate Therapeutics, Genentech, Innate Pharma, Kite (a Gilead company), MEI Pharma, Merck, MorphoSys/Incyte, Mustang Bio, Pharmacyclics, Regeneron, Sound Biologics, and TG Therapeutics; and reports research funding from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Atara Biotherapeutics, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Genentech, Genmab, Gilead, MorphoSys/Incyte, Mustang Bio, Pharmacyclics, Sunesis, and TG Therapeutics. L.G. received honorarium from Bristol Myers Squibb. M.B.A. received research funding from Ansun, BioPharma Inc, and Janssen. S.H. had employment with Adaptive Biotechnologies. N.S.M. had employment with, and stock or other ownership in, HCA Healthcare; and reports a consulting/advisory role for Anthem, Inc. M.A.K.-D. received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pharmacyclics, and Novartis. T.B. had stock or other ownership in Aprea Therapeutics; received honoraria from Pfizer Hematology-Oncology; and reports research funding from Mayo Clinic, Cancer Center Support Grant. Y.L. reports a consulting/advisory role for Kite/Gilead, Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb, Juno/Bristol Myers Squibb, bluebird bio, Janssen, Legend Biotech, Gamida Cell, Novartis, Iovance, Takeda, Fosun Kite, and Pfizer; and received research funding from Kite/Gilead, Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb, bluebird bio, Janssen, Legend Biotech, Merck, Takeda, and Boston Scientific. N.N.B. had a consulting/advisory role for Acrotech, Affimed, Astellas, Kymera, and Secura Bio; and received research funding from Affimed, Daiichi Sankyo, and Kite (a Gilead company). Z.-H.H. had employment with Kite (a Gilead company); and stock or other ownership in Gilead Sciences. H.-L.W. had employment with Kite (a Gilead company). A.B. had employment with, and stock or other ownership in, Gilead Sciences. E.B. had employment with, stock or other ownership in, and consulting/advisory role for, Kite (a Gilead company). H.M. had employment with Kite (a Gilead company); and stock or ownership in Gilead Sciences. C.S. had employee with Kite (a Gilead company); and stock or other ownership in Gilead Sciences. H.X. had employment with Kite (a Gilead company). M.C.P. received honoraria from Celgene; reports consulting/advisory role for Amgen, Medigene, and Pfizer; and reports research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Kite (a Gilead company), and Novartis. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
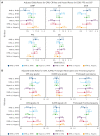
Comment in
-
Axi-cel outcomes among non-Hispanic Black patients.Blood. 2024 Jun 27;143(26):2681-2682. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024024959. Blood. 2024. PMID: 38935357 No abstract available.
References
-
- Klink AJ, Nabhan C, Hyung Lee C, et al. Real-world management and outcomes of patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated in the United States. J Clin Pathways. 2020;6(1):44–53.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01 CA152108/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI158861/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HL138660/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL155741/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- OT3 HL147741/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- SC1 MH093181/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069197/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA262613/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA233032/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA218285/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA121947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA231838/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL128568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA076518/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA231141/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA100019/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HL069246/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI150999/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL131731/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI126612/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HL157560/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA262899/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI128775/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA244328/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA111412/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

