Awake versus Asleep Anesthesia in Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38636468
- PMCID: PMC11152021
- DOI: 10.1159/000536310
Awake versus Asleep Anesthesia in Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a well-established surgical therapy for patients with Parkinsons' Disease (PD). Traditionally, DBS surgery for PD is performed under local anesthesia, whereby the patient is awake to facilitate intraoperative neurophysiological confirmation of the intended target using microelectrode recordings. General anesthesia allows for improved patient comfort without sacrificing anatomic precision and clinical outcomes.
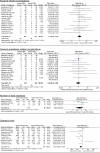
Methods: We performed a systemic review and meta-analysis on patients undergoing DBS for PD. Published randomized controlled trials, prospective and retrospective studies, and case series which compared asleep and awake techniques for patients undergoing DBS for PD were included. A total of 19 studies and 1,900 patients were included in the analysis.
Results: We analyzed the (i) clinical effectiveness - postoperative UPDRS III score, levodopa equivalent daily doses and DBS stimulation requirements. (ii) Surgical and anesthesia related complications, number of lead insertions and operative time (iii) patient's quality of life, mood and cognitive measures using PDQ-39, MDRS, and MMSE scores. There was no significant difference in results between the awake and asleep groups, other than for operative time, for which there was significant heterogeneity.
Conclusion: With the advent of newer technology, there is likely to have narrowing differences in outcomes between awake or asleep DBS. What would therefore be more important would be to consider the patient's comfort and clinical status as well as the operative team's familiarity with the procedure to ensure seamless transition and care.
Keywords: Anesthesia; Central nervous system disease; Deep brain stimulation; Electric stimulation; Movement disorders; Parkinson disease.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Lefranc M, Zouitina Y, Tir M, Merle P, Ouendo M, Constans JM, et al. Asleep robot-assisted surgery for the implantation of subthalamic electrodes provides the same clinical improvement and therapeutic window as awake surgery. World Neurosurg. 2017;106:602–8. - PubMed
-
- Maltête D, Navarro S, Welter ML, Roche S, Bonnet AM, Houeto JL, et al. Subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson disease: with or without anesthesia? Arch Neurol. 2004;61(3):390–2. - PubMed
-
- Yamada K, Goto S, Kuratsu J, Matsuzaki K, Tamura T, Nagahiro S, et al. Stereotactic surgery for subthalamic nucleus stimulation under general anesthesia: a retrospective evaluation of Japanese patients with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2007;13(2):101–7. - PubMed
-
- Chen T, Mirzadeh Z, Chapple KM, Lambert M, Shill HA, Moguel-Cobos G, et al. Clinical outcomes following awake and asleep deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg. 2018;130(1):109–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

