Lateralising reverse shoulder arthroplasty using bony increased offset (BIO-RSA) or increasing glenoid component diameter: comparison of clinical, radiographic and patient reported outcomes in a matched cohort
- PMID: 38637350
- PMCID: PMC11026328
- DOI: 10.1186/s10195-024-00764-4
Lateralising reverse shoulder arthroplasty using bony increased offset (BIO-RSA) or increasing glenoid component diameter: comparison of clinical, radiographic and patient reported outcomes in a matched cohort
Abstract
Background: This study aims to compare the range of motion (ROM) of reverse shoulder arthroplasty lateralised by bony increased offset (BIO-RSA) using a standard 38-mm (mm) component to regular reverse shoulder arthroplasty (RSA) lateralised by using a 42-mm glenoid component. The secondary aims are to compare patient-reported and radiographic outcomes between the two groups.
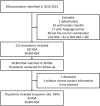
Materials and methods: All patients with a BIO-RSA and size 38 glenosphere were retrospectively identified and matched to patients with a regular RSA and size 42 glenosphere. Matched patients were invited for a follow-up visit. ROM was assessed as well as radiographic outcomes (lateralisation, distalisation, inferior overhang, scapular notching, heterotopic bone formation, radiolucency, stress shielding, bone graft healing and viability and complications) and patient-reported outcomes (subjective shoulder value, Constant score, American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons, activities of daily living which require internal rotation, activities of daily living which require external rotation and a visual analogue scale for pain). Outcomes were compared between the two groups.
Results: In total, 38 BIO-RSAs with a size 38 glenosphere were matched to 38 regular RSAs with a size 42 glenosphere. Of the 76 matched patients, 74 could be contacted and 70 (95%) were included. At the final follow-up, there were no differences between the two groups in ROM, patient-reported outcomes or radiographic outcomes (p > 0.485).
Conclusions: Using a larger glenosphere is a feasible alternative to BIO-RSA for lateralising RSA, providing comparable ROM, patient-reported and radiographic results, while potentially decreasing costs, operative time and complication rates.
Keywords: Bony increased offset reverse shoulder arthroplasty; Patient-reported outcomes; Range of motion.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AAM declares no competing interests; GAB provided consultancy services for Stryker; MK declares no competing interests; TL declares no competing interests; DE declares no competing interests; MvdB declares no competing interests; LL received royalties from Depuy and provided consultancy services for Stryker and Smith and Nephew; TL provided consultancy for Depuy, Stryker and Smith and Nephew. This study received no funding or other forms of support.
Similar articles
-
Bony increased-offset-reverse shoulder arthroplasty: 5 to 10 years' follow-up.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020 Oct;29(10):2111-2122. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2020.02.008. Epub 2020 Jun 4. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020. PMID: 32505414
-
Clinical results of bony increased-offset reverse shoulder arthroplasty (BIO-RSA) associated with an onlay 145° curved stem in patients with cuff tear arthropathy: a comparative study.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020 Jan;29(1):58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2019.05.023. Epub 2019 Aug 7. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020. PMID: 31401130
-
Does bony increased-offset reverse shoulder arthroplasty decrease scapular notching?J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015 Mar;24(3):468-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2014.08.015. Epub 2014 Oct 22. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015. PMID: 25441556
-
Does isolated glenosphere lateralization affect outcomes in reverse shoulder arthroplasty?Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2023 Jun;109(4):103401. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2022.103401. Epub 2022 Sep 13. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 36108822 Review.
-
Lateralized versus nonlateralized glenospheres in reverse shoulder arthroplasty: a systematic review with meta-analysis.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021 Jul;30(7):1700-1713. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2020.09.041. Epub 2020 Nov 4. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021. PMID: 33160029
Cited by
-
Accuracy of implant placement after preoperative planning using Blueprint software in inlay and onlay reverse total shoulder arthroplasty systems: a cadaver study.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2025 Jun 26:S1058-2746(25)00488-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2025.05.019. Online ahead of print. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2025. PMID: 40581086
-
Impact of systemic lupus erythematosus on adverse outcomes and readmission after total shoulder arthroplasty: a Nationwide Readmission Database analysis 2016-2020.J Orthop Traumatol. 2025 Jun 21;26(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s10195-025-00858-7. J Orthop Traumatol. 2025. PMID: 40542928 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources