Disruption of the pro-oncogenic c-RAF-PDE8A complex represents a differentiated approach to treating KRAS-c-RAF dependent PDAC
- PMID: 38637546
- PMCID: PMC11026450
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-59451-3
Disruption of the pro-oncogenic c-RAF-PDE8A complex represents a differentiated approach to treating KRAS-c-RAF dependent PDAC
Abstract
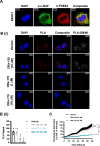
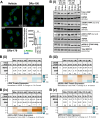
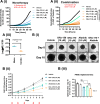
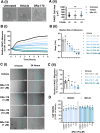
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is considered the third leading cause of cancer mortality in the western world, offering advanced stage patients with few viable treatment options. Consequently, there remains an urgent unmet need to develop novel therapeutic strategies that can effectively inhibit pro-oncogenic molecular targets underpinning PDACs pathogenesis and progression. One such target is c-RAF, a downstream effector of RAS that is considered essential for the oncogenic growth and survival of mutant RAS-driven cancers (including KRASMT PDAC). Herein, we demonstrate how a novel cell-penetrating peptide disruptor (DRx-170) of the c-RAF-PDE8A protein-protein interaction (PPI) represents a differentiated approach to exploiting the c-RAF-cAMP/PKA signaling axes and treating KRAS-c-RAF dependent PDAC. Through disrupting the c-RAF-PDE8A protein complex, DRx-170 promotes the inactivation of c-RAF through an allosteric mechanism, dependent upon inactivating PKA phosphorylation. DRx-170 inhibits cell proliferation, adhesion and migration of a KRASMT PDAC cell line (PANC1), independent of ERK1/2 activity. Moreover, combining DRx-170 with afatinib significantly enhances PANC1 growth inhibition in both 2D and 3D cellular models. DRx-170 sensitivity appears to correlate with c-RAF dependency. This proof-of-concept study supports the development of DRx-170 as a novel and differentiated strategy for targeting c-RAF activity in KRAS-c-RAF dependent PDAC.
Keywords: Disruptor peptide; KRAS; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; Protein–protein interaction; c-RAF-PDE8A.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
CMB and GSB hold patent rights to relevant published work. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

