Development and validation of the rheumatoid arthritis scale among the system of quality of life instruments for chronic diseases QLICD-RA (V2.0)
- PMID: 38637566
- PMCID: PMC11026454
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-58910-1
Development and validation of the rheumatoid arthritis scale among the system of quality of life instruments for chronic diseases QLICD-RA (V2.0)
Abstract
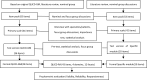
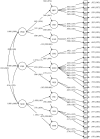
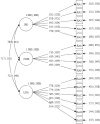
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a more serious threatening to people and suitable for QOL measurement. A few specific QOL instruments are available without considering Chinese culture. The present study was aimed to develop and validate the Rheumatoid Arthritis Scale among the System of Quality of Life Instruments for Chronic Diseases (QLICD-RA V2.0). The data collected from 379 patients with RA was used to evaluate the psychometric properties of the scale. The reliability was evaluated by the internal consistency Cronbach's α, test-retest reliability Pearson correlation r and intra-class correlation (ICC). We evaluated the construct validity and criteria-related validity by correlation analysis and structural equation modeling. We compared the differences in scores of QLICD-RA before and after treatment and used the Standard Response Mean (SRM) to assess the responsiveness. The results showed that the internal consistency coefficient Cronbach's α values were greater than 0.70. The correlations r and ICCs were greater than 0.80. The correlation analysis and structural equation modeling confirmed good construct validity and criterion-related validity. The SRM ranges from 0.07 to 0.27 for significant domains/facets. It concluded that QLICD-RA (2.0) is a reliable and valid instrument to measure QOL among patients with RA.
Keywords: Instrument; Quality of life; Rheumatoid arthritis; Validation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and validation of the osteoporosis scale among the system of quality of life instruments for chronic diseases QLICD-OS (V2.0).BMC Geriatr. 2024 May 7;24(1):407. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05019-9. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38714958 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of the psoriasis scale among the system of quality of life instruments for chronic diseases QLICD-PS (V2.0).Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022 Apr 22;20(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12955-022-01970-6. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022. PMID: 35459208 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of quality of life instruments for chronic diseases-Chronic gastritis version 2 (QLICD-CG V2.0).PLoS One. 2018 Nov 14;13(11):e0206280. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206280. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30427879 Free PMC article.
-
Instruments for Measuring Self-Efficacy in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review.Nurs Health Sci. 2025 Jun;27(2):e70133. doi: 10.1111/nhs.70133. Nurs Health Sci. 2025. PMID: 40390556
-
[Psychometric characteristics of questionnaires designed to assess the knowledge, perceptions and practices of health care professionals with regards to alcoholic patients].Encephale. 2004 Sep-Oct;30(5):437-46. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95458-9. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15627048 Review. French.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Chronic rheumatic conditions. Retrieved from 7 February 2020. https://www.who.int/chp/topics/rheumatic/en/
-
- Ometto F, Fedeli U, Schievano E, et al. Cause-specific mortality in a large population-based cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Italy. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018;36(4):636–642. - PubMed
-
- Zeng XF, Zhu SL, Tan AC, et al. Disease burden and quality of life of rheumatoid arthritis in China: A systematic review. Chin. J. Evid. Based Med. 2013;13(3):300–307.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical