Statine-based peptidomimetic compounds as inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 main protease (SARS-CoV‑2 Mpro)
- PMID: 38637583
- PMCID: PMC11026380
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-59442-4
Statine-based peptidomimetic compounds as inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 main protease (SARS-CoV‑2 Mpro)
Abstract
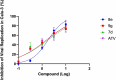
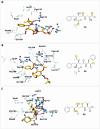
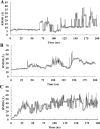
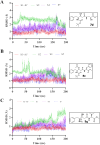
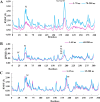
COVID-19 is a multisystemic disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 airborne virus, a member of the Coronaviridae family. It has a positive sense single-stranded RNA genome and encodes two non-structural proteins through viral cysteine-proteases processing. Blocking this step is crucial to control virus replication. In this work, we reported the synthesis of 23 statine-based peptidomimetics to determine their ability to inhibit the main protease (Mpro) activity of SARS-CoV-2. Among the 23 peptidomimetics, 15 compounds effectively inhibited Mpro activity by 50% or more, while three compounds (7d, 8e, and 9g) exhibited maximum inhibition above 70% and IC50 < 1 µM. Compounds 7d, 8e, and 9g inhibited roughly 80% of SARS-CoV-2 replication and proved no cytotoxicity. Molecular docking simulations show putative hydrogen bond and hydrophobic interactions between specific amino acids and these inhibitors. Molecular dynamics simulations further confirmed the stability and persisting interactions in Mpro's subsites, exhibiting favorable free energy binding (ΔGbind) values. These findings suggest the statine-based peptidomimetics as potential therapeutic agents against SARS-CoV-2 by targeting Mpro.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

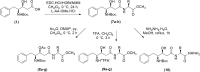
Similar articles
-
In-silico guided design, screening, and molecular dynamic simulation studies for the identification of potential SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors for the targeted treatment of COVID-19.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Feb-Mar;42(4):1733-1750. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2202247. Epub 2023 Apr 28. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37114441
-
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro: A Potential Target for Peptidomimetics and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 19;11(4):607. doi: 10.3390/biom11040607. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33921886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycyrrhizic acid conjugates with amino acid methyl esters target the main protease, exhibiting antiviral activity against wild-type and nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants.Antiviral Res. 2024 Jul;227:105920. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105920. Epub 2024 May 29. Antiviral Res. 2024. PMID: 38821317
-
Structure-based lead optimization of herbal medicine rutin for inhibiting SARS-CoV-2's main protease.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2020 Nov 21;22(43):25335-25343. doi: 10.1039/d0cp03867a. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2020. PMID: 33140777
-
Taming the storm: potential anti-inflammatory compounds targeting SARS-CoV-2 MPro.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Oct;32(5):3007-3035. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01525-9. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39048773 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in Research on Inhibitors Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro).ACS Omega. 2024 Aug 2;9(32):34196-34219. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c03023. eCollection 2024 Aug 13. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39157135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Structural Investigation of the Interaction between a GC-376-Based Peptidomimetic PROTAC and Its Precursor with the Viral Main Protease of Coxsackievirus B3.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 6;14(10):1260. doi: 10.3390/biom14101260. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456193 Free PMC article.
-
Statine-based peptidomimetics as SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like protease inhibitors: in Silico and in vitro studies.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 20;15(1):26319. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11599-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40685447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO; World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/ (2023).
-
- NIH; National Institutes of Health. COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. 2023https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/about-the-guidelines/what.... - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

