Effectiveness of intravitreal ranibizumab for diabetic macular edema in vitrectomized versus non-vitrectomized eyes: a Meta-analysis
- PMID: 38638245
- PMCID: PMC10988062
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2024.04.18
Effectiveness of intravitreal ranibizumab for diabetic macular edema in vitrectomized versus non-vitrectomized eyes: a Meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of intravitreal ranibizumab (IVR) for diabetic macular edema (DME) in vitrectomized versus non-vitrectomized eyes.
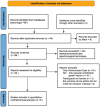
Methods: The PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane, EBSCO were comprehensively searched for studies comparing vitrectomized and non-vitrectomized eyes with DME. Clinical outcomes of best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), central macular thickness (CMT), the mean number of intravitreal injection and adverse events were extracted and analyzed.
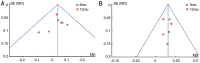
Results: Six studies involving 641 eyes were included. Final visual gain significantly improved and CMT significantly reduced in vitrectomized eyes at 6mo and 12mo visits (P<0.05). Although the mean reduction in CMT among non-vitrectomized eyes was significantly greater than in vitrectomized eyes at the 6mo [mean difference (MD)=53.57, 95% confidence interval (CI): 28.03 to 78.72, P<0.0001] and 12mo (MD=49.65, 95%CI: 19.58 to 79.72, P=0.01), no significant difference was detected in improvement in BCVA at either 6mo (MD=0.05, 95%CI: -0.02 to 0.13, P=0.14) or 12mo (MD=0.03, 95%CI: -0.04 to 0.09, P=0.43). Injection number of ranibizumab in non-vitrectomized eyes was significantly less than that in vitrectomized eyes during 6-month period (MD=0.60, 95%CI: 0.16 to 1.04, P=0.008), while there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups during 12mo of follow-up.
Conclusion: Evidence from current study suggests that IVR was useful for both vitrectomized group and non-vitrectomized group with DME. Although less reduction in macular thickness is found in vitrectomized group, visual improvement between two groups is similar.
Keywords: diabetic macular edema; ranibizumab; vitrectomized eye.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Wang YH, None; Xu Q, None; Luan J, None.
Figures

References
-
- Guo HX, Li WB, Nie ZT, Zhang X, Jiao MF, Bai SQ, Duan NX, Li XR, Hu BJ. Microinvasive pars Plana vitrectomy combined with internal limiting membrane peeling versus anti-VEGF intravitreal injection for treatment-naïve diabetic macular edema (VVV-DME study):study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2023;24(1):685. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Teo ZL, Tham YC, Yu M, et al. Global prevalence of diabetic retinopathy and projection of burden through 2045:systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2021;128(11):1580–1591. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell P, Bandello F, Schmidt-Erfurth U, Lang GE, Massin P, Schlingemann RO, Sutter F, Simader C, Burian G, Gerstner O, Weichselberger A, RESTORE study group The RESTORE study: ranibizumab monotherapy or combined with laser versus laser monotherapy for diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. 2011;118(4):615–625. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
