Robotic systems for upper-limb rehabilitation in multiple sclerosis: a SWOT analysis and the synergies with virtual and augmented environments
- PMID: 38638271
- PMCID: PMC11025362
- DOI: 10.3389/frobt.2024.1335147
Robotic systems for upper-limb rehabilitation in multiple sclerosis: a SWOT analysis and the synergies with virtual and augmented environments
Abstract
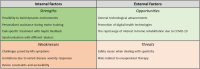
The robotics discipline is exploring precise and versatile solutions for upper-limb rehabilitation in Multiple Sclerosis (MS). People with MS can greatly benefit from robotic systems to help combat the complexities of this disease, which can impair the ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs). In order to present the potential and the limitations of smart mechatronic devices in the mentioned clinical domain, this review is structured to propose a concise SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) Analysis of robotic rehabilitation in MS. Through the SWOT Analysis, a method mostly adopted in business management, this paper addresses both internal and external factors that can promote or hinder the adoption of upper-limb rehabilitation robots in MS. Subsequently, it discusses how the synergy with another category of interaction technologies - the systems underlying virtual and augmented environments - may empower Strengths, overcome Weaknesses, expand Opportunities, and handle Threats in rehabilitation robotics for MS. The impactful adaptability of these digital settings (extensively used in rehabilitation for MS, even to approach ADL-like tasks in safe simulated contexts) is the main reason for presenting this approach to face the critical issues of the aforementioned SWOT Analysis. This methodological proposal aims at paving the way for devising further synergistic strategies based on the integration of medical robotic devices with other promising technologies to help upper-limb functional recovery in MS.
Keywords: SWOT; augmented reality; digital health; multiple sclerosis; rehabilitation; robotics; virtual reality.
Copyright © 2024 Albanese, Bucchieri, Podda, Tacchino, Buccelli, De Momi, Laffranchi, Mannella, Holmes, Zenzeri, De Michieli, Brichetto and Barresi.
Conflict of interest statement
GA and JZ were employed by ReWing s r l. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Albanese G. A., Zenzeri J., De Santis D. (2023). The effect of feedback modality when learning a novel wrist sensorimotor transformation through a body machine interface. IEEE. - PubMed
-
- Althnian A., AlSaeed D., Al-Baity H., Samha A., Dris A. B., Alzakari N., et al. (2021). Impact of dataset size on classification performance: an empirical evaluation in the medical domain. Appl. Sci. 11, 796. 10.3390/app11020796 - DOI
-
- Arafat I. M., Ferdous S. M. S., Quarles J. (2016). “The effects of cybersickness on persons with multiple sclerosis,” in Proceedings of the 22nd ACM conference on virtual reality software and technology, 51–59.
-
- Araujo H. A. G. d. O., Souza R. J. d., da Silva T. C. O., Nascimento T. S., Terra M. B., Smaili S. M. (2023). Immediate effect of augmented reality, virtual reality, and neurofunctional physiotherapy on postural control and executive function of individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Games Health J. 12, 211–219. 10.1089/g4h.2021.0222 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

