Drug-Induced Atypical Lipodystrophy
- PMID: 38638337
- PMCID: PMC11025636
- DOI: 10.1210/jcemcr/luae067
Drug-Induced Atypical Lipodystrophy
Abstract
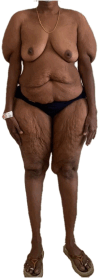
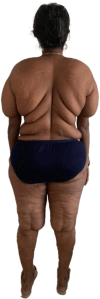
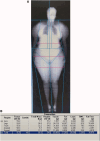
We describe a case of an Asian-Indian female patient who presented to us with abnormal fat accumulations in the torso and upper arms following indiscriminate use of corticosteroid and anabolic steroids for about 7 years. Despite prolonged steroid use, the patient did not display cushingoid phenotype or metabolic decompensation. Bone density, echocardiography, and ultrasonogram of the liver were also normal with no evidence of excess pericardial fat, hepatic steatosis, or peliosis hepatis. Concurrent use of anabolic androgen is thought to be protective against the ill effects of steroids, especially on the muscle and bone. This phenomenon has been observed in children and adolescents with Cushing syndrome where the adrenal androgen excess and increased physical activity have shown to reasonably reduce protein catabolism and help in preserving muscle and bone mass. The patient was withdrawn from the drugs and was put on replacement hydrocortisone that was gradually tapered over the next few weeks and planned for surgical correction. This case highlights the fact that medical providers should be aware that a combination of anabolic steroids and glucocorticoids are still used for weight-building purposes, and these patients may present with atypical signs/symptoms as a result of this combination of drugs.
Keywords: anabolic steroids; atypical lipodystrophy; drug-induced lipodystrophy; steroid abuse; steroid effects.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Hartgens F, van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Ebbing S, Vollaard N, Rietjens G, Kuipers H. Androgenic-anabolic steroid-induced body changes in strength athletes. Phys Sportsmed. 2001;29(1):49‐65. - PubMed
-
- Enzi G, Busetto L, Sergi G, et al. . Multiple symmetric lipomatosis: a rare disease and its possible links to brown adipose tissue. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015;25(4):347‐353. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
