Treatment Options for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Immunotherapy: Present and Future
- PMID: 38638377
- PMCID: PMC11022065
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2023.00462
Treatment Options for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Immunotherapy: Present and Future
Abstract
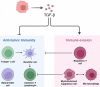
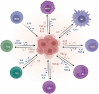
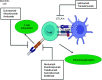
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common cancer, and the body's immune responses greatly affect its progression and the prognosis of patients. Immunological suppression and the maintenance of self-tolerance in the tumor microenvironment are essential responses, and these form part of the theoretical foundations of immunotherapy. In this review, we first discuss the tumor microenvironment of HCC, describe immunosuppression in HCC, and review the major biomarkers used to track HCC progression and response to treatment. We then examine antibody-based therapies, with a focus on immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), monoclonal antibodies that target key proteins in the immune response (programmed cell death protein 1, anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4, and programmed death-ligand 1) which have transformed the treatment of HCC and other cancers. ICIs may be used alone or in conjunction with various targeted therapies for patients with advanced HCC who are receiving first-line treatments or subsequent treatments. We also discuss the use of different cellular immunotherapies, including T cell receptor (TCR) T cell therapy and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy. We then review the use of HCC vaccines, adjuvant immunotherapy, and oncolytic virotherapy, and describe the goals of future research in the development of treatments for HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Immunotherapy; Liver cancer; Vaccines.
© 2024 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Strategies to Improve the Antitumor Effect of Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 26;12:783236. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.783236. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34899747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments with immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018 Aug;18(8):905-910. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2018.1499722. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29995439 Review.
-
Novel antigens for targeted radioimmunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Jan;478(1):23-37. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04483-4. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 35708866 Review.
-
Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current status and future perspectives.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Feb 14;29(6):1054-1075. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.1054. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36844141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Immunosuppressive Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 28;22(11):5801. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115801. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34071550 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of Immune Cell Roles in Breast Cancer Immunotherapy.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025 May;8(5):e70217. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.70217. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 40356222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oleanolic Acid Restores Drug Sensitivity in Sorafenib-resistant Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Evidence from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2025 Jun 28;13(6):469-483. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2024.00369. Epub 2025 Apr 18. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40474884 Free PMC article.
-
Modern therapeutic approaches for hepatic tumors: progress, limitations, and future directions.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 30;16(1):959. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02773-z. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40445470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: mechanistic insights and therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine.Mol Cancer. 2025 Jun 10;24(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02378-8. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40495147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a review of current and emerging approaches.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 20;16:1533874. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1533874. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40621467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
