Modification of a Selective NTRK2 Agonist and Confirmation of Activity in a Glaucoma-on-a-Chip Model
- PMID: 38638624
- PMCID: PMC11022028
- DOI: 10.18502/jovr.v19i1.15439
Modification of a Selective NTRK2 Agonist and Confirmation of Activity in a Glaucoma-on-a-Chip Model
Abstract
Purpose: RNYK is a selective agonist of the neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 2 (NTRK2) which has been screened from a phage-displayed peptide library. Its sequence is SGVYKVAYDWQH, similar to a native NTRK2 ligand, that is, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). The current study was performed to recognize and confirm critical residues for RNYK activity in a glaucoma-on-a-chip model.
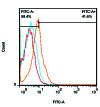
Methods: We designed a modified RNYK (mRNYK) peptide based on hotspots of the RNYK sequence identified by alanine scanning. The critical residues consisted of tyrosine, valine, aspartic acid, and tryptophan (YVDW); however, lysine and glutamine were also maintained in the final sequence (YKVDWQ) for forming amide bonds and peptide dimerization. The affinity of mRNYK binding was confirmed by testing against NTRK2 receptors on the surface of ATRA-treated SH-SY5Y cells. The neuroprotective effect of mRNYK was also evaluated in cell culture after elevated pressure insult in a glaucoma-on-a-chip model.
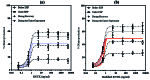
Results: The primary amine on the lysine side-chain from one sequence (YKVDWQ) reacted with a γ-carboxamide group of glutamine from the other sequence, forming dimeric mRNYK. In silico, molecular dynamic simulations of the mRNYK-NTRK2 complex showed more stable and stronger interactions as compared to the RNYK-NTRK2 complex. In vitro, mRNYK demonstrated a neuroprotective effect on SH-SY5Y cells under normal and elevated pressure comparable to RNYK. The 50% effective concentration (logEC50) for mRNYK was 0.7009, which was better than RNYK with a logEC50 of 0.8318.
Conclusion: The modified peptide studied herein showed improved stability over the original peptide (RNYK) and demonstrated potential for use as a BDNF agonist with neuroprotective properties for treatment of neurodegenerative disorders such as glaucoma.
Keywords: Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor; Neuroprotection; Neurotrophic Tyrosine Receptor Kinase; Agonist.
Copyright © 2024 Nafian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures






References
-
- Soppet D, Escandon E, Maragos J, Middlemas DS, Raid SW, Blair J, et al. The neurotrophic factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 are ligands for the trkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1991;65:895–903. - PubMed
-
- Carter BD, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B, Offenhäuser N, Böhm-Matthaei R, Baeuerle PA, et al. Selective activation of NF-κB by nerve growth factor through the neurotrophin receptor p75. Science. 1996;272:542–545. - PubMed
-
- Banfield MJ, Naylor RL, Robertson AG, Allen SJ, Dawbarn D, Brady RL. Specificity in Trk receptor: Neurotrophin interactions: The crystal structure of TrkB-d5 in complex with neurotrophin-4/5. Structure. 2001;9:1191–1199. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan DR, Miller FD. Neurotrophin signal transduction in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000;10:381–391. - PubMed
-
- Barker PA. p75NTR is positively promiscuous: Novel partners and new insights. Neuron. 2004;42:529–533. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
