Necrotizing Pneumonia With Extensive Lobar Cavitation
- PMID: 38638719
- PMCID: PMC11024767
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.56437
Necrotizing Pneumonia With Extensive Lobar Cavitation
Abstract
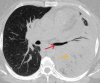
Pneumonia occupies one of the leading positions in morbidity and mortality worldwide. It is frequently categorized depending on the site of acquisition. Here, we present a case of a young woman who was admitted to the Emergency Department (ED) with cough, dyspnea, fever, and progressive worsening associated with palpitations and hypotension. An initial x-ray was followed by a computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest, which revealed signs of extensive left lung pneumonia with pleural effusion. Despite initial improvement after antibiotic treatment, the patient's condition declined. A repeat chest CT showed evidence of extensive lobar cavitations, leading to suspicion of tuberculosis.
Keywords: cavitation; dyspnea; necrotizing pneumonia; pleural effusion; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2024, Suleac et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Deaths: final data for 2013. Xu J, Murphy SL, Kochanek KD, et al. https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/40133. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2016;64:1. - PubMed
-
- Aspiration pneumonia, necrotizing pneumonia, and lung abscess. Pennza PT. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 1989;7:279. - PubMed
-
- Necrotising pneumonia is an increasingly detected complication of pneumonia in children. Sawicki GS, Lu FL, Valim C, Cleveland RH, Colin AA. Eur Respir J. 2008;31:1285–1291. - PubMed
-
- Retrospective study in children with necrotizing pneumonia: nine years of intensive care experience. Blanco-Iglesias E, Oñoro G, Almodovar-Martín JL, et al. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020;39:571–575. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
