Medically Managed Lyme Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Case Report
- PMID: 38638742
- PMCID: PMC11025306
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.56457
Medically Managed Lyme Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Case Report
Abstract
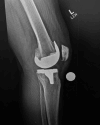
Arthritis associated with Lyme disease is frequent in regions of the United States where the illness is widespread; nonetheless, periprosthetic joint infections (PJI) caused by Lyme are exceptionally rare. As of October 2023, only five cases of Lyme PJI have been documented in the literature. Four of these cases were managed successfully with surgical intervention, while one was managed successfully with oral and IV antibiotics. Because of limited documented cases, there are no recommended treatment guidelines. This has left physicians trying to blend the treatment guidelines for Lyme arthritis, which is medically managed with antibiotics, and PJIs, which involve invasive surgical procedures. The patient in this case presented with a common presentation of acute Lyme arthritis, but it was complicated by a previous total knee arthroplasty. Treatment of this patient included three months of doxycycline 100mg BID, which resulted in complete resolution of symptoms.
Keywords: lyme arthritis; periprosthetic joint infection; pji; tka; total knee arthroplasty.
Copyright © 2024, Saar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- The clinical assessment, treatment, and prevention of lyme disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and babesiosis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Wormser GP, Dattwyler RJ, Shapiro ED, et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:1089–1134. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials