Lectins as the prominent potential to deliver bioactive metal nanoparticles by recognizing cell surface glycans
- PMID: 38638961
- PMCID: PMC11024627
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29394
Lectins as the prominent potential to deliver bioactive metal nanoparticles by recognizing cell surface glycans
Abstract
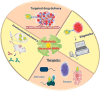
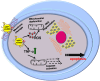
Lectins are renowned for recognizing specific carbohydrates, but there is evidence that they can bind to other endogenous ligands. Therefore, lectin can be used as a carrier to recognize glycoconjugates on the cell surface. The anticancer, antibacterial, and immunomodulatory properties of some lectins are established. Metal nanoparticles (MNPs) have been used in various fields recently, but their documented toxicity has raised questions about their suitability for biomedical uses. The advantages of MNPs can be realized if we deliver the NPs to the site of action; as a result, NPs may achieve greater therapeutic efficiency at lower doses with less toxicity. The use of carbohydrate specificity by lectin MNPs conjugates for diagnostics and therapeutics was addressed. The review summarised the multidimensional application of lectins and described their potential for delivery of MNPs in future drug development.
Keywords: Anticancer; Antimicrobial; Drug delivery; Lectins; Metal nanoparticles.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction of sugar stabilised silver nanoparticles with Momordica charantia seed lectin, a type II ribosome inactivating protein.Glycoconj J. 2023 Apr;40(2):179-189. doi: 10.1007/s10719-023-10107-w. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Glycoconj J. 2023. PMID: 36800135
-
Glycan-Gold Nanoparticles as Multifunctional Probes for Multivalent Lectin-Carbohydrate Binding: Implications for Blocking Virus Infection and Nanoparticle Assembly.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Oct 21;142(42):18022-18034. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c06793. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 32935985
-
[The human lectin supersystems possessing probiotic and protective actions.].Klin Lab Diagn. 2020;65(4):231-238. doi: 10.18821/0869-2084-2020-65-4-231-238. Klin Lab Diagn. 2020. PMID: 32227729 Review. Russian.
-
Lectin-Carbohydrate Interactions: Implications for the Development of New Anticancer Agents.Curr Med Chem. 2017 Nov 17;24(34):3667-3680. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170523110400. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28545372 Review.
-
Metal nanoparticles and carbohydrate polymers team up to improve biomedical outcomes.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Dec;168:115695. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115695. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37839113 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Oral Biomacromolecule Therapies for Metabolic Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 12;17(2):238. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020238. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40006605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
F-type lectins: Structural and functional aspects, and potential biomedical applications.BBA Adv. 2025 Jun 14;8:100166. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2025.100166. eCollection 2025. BBA Adv. 2025. PMID: 40612915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sahu T., Ratre Y.K., Chauhan S., Bhaskar L.V.K.S., Nair M.P., Verma H.K. Nanotechnology based drug delivery system: current strategies and emerging therapeutic potential for medical science. J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 2021;63 doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102487. - DOI
-
- Naisbett B., Woodley J. The potential use of tomato lectin for oral drug delivery: 3. Bioadhesion in vivo. Int. J. Pharm. 1995;114(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0378-5173(94)00242-W. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

