Current trends in clinical trials and the development of small molecule epigenetic inhibitors as cancer therapeutics
- PMID: 38639711
- PMCID: PMC11233149
- DOI: 10.2217/epi-2023-0443
Current trends in clinical trials and the development of small molecule epigenetic inhibitors as cancer therapeutics
Abstract
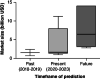
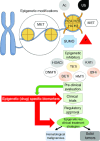
Epigenetic mechanisms control and regulate normal chromatin structure and gene expression patterns, with epigenetic dysregulation observed in many different cancer types. Importantly, epigenetic modifications are reversible, offering the potential to silence oncogenes and reactivate tumor suppressors. Small molecule drugs manipulating these epigenetic mechanisms are at the leading edge of new therapeutic options for cancer treatment. The clinical use of histone deacetyltransferases inhibitors (HDACi) demonstrates the effectiveness of targeting epigenetic mechanisms for cancer treatment. Notably, the development of new classes of inhibitors, including lysine acetyltransferase inhibitors (KATi), are the future of epigenetic-based therapeutics. We outline the progress of current classes of small molecule epigenetic drugs for use against cancer (preclinical and clinical) and highlight the potential market growth in epigenetic-based therapeutics.
Keywords: HAT; KAT; acetyltransferase; cancer; epigenetic; inhibitor; lysine; precision; small molecule; targeted; therapeutic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests or relevant affiliations with any organization or entity with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting cancer using KAT inhibitors to mimic lethal knockouts.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Aug 15;44(4):979-86. doi: 10.1042/BST20160081. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27528742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patent spotlight: small-molecule lysine acetyltransferase inhibitors (KATi).Pharm Pat Anal. 2020 Jan;9(1):17-28. doi: 10.4155/ppa-2019-0025. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Pharm Pat Anal. 2020. PMID: 32008421
-
Targeting Epigenetic Regulatory Enzymes for Cancer Therapeutics: Novel Small-Molecule Epidrug Development.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 28;12:848221. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.848221. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35419278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting epigenetic regulation for cancer therapy using small molecule inhibitors.Adv Cancer Res. 2023;158:73-161. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2023.01.001. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Adv Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36990539 Review.
-
Histone lysine acetyltransferase inhibitors: an emerging class of drugs for cancer therapy.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2024 Mar;45(3):243-254. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2024.01.010. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38383216 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the Cellular Roles of the Lysine Acetyltransferase Tip60 in Cancer: A Multi-Action Molecular Target for Precision Oncology.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 27;16(15):2677. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152677. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Plasmodium falciparum histone methyltransferase SET10 participates in a chromatin modulation network crucial for intraerythrocytic development.mSphere. 2024 Nov 21;9(11):e0049524. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00495-24. Epub 2024 Oct 24. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39445823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh M, Kumar V, Sehrawat Net al. . Current paradigms in epigenetic anticancer therapeutics and future challenges. Semin. Cancer Biol. 83, 422–440 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources