Exploring the mechanism of Tingli Pill in the treatment of HFpEF based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- PMID: 38640300
- PMCID: PMC11029988
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037727
Exploring the mechanism of Tingli Pill in the treatment of HFpEF based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
Abstract
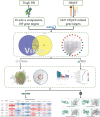
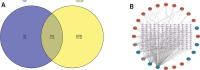
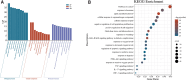
To explore the mechanism of action of Tingli Pill (TLP) in the treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) by using network pharmacology and molecular docking technology. The active components and targets of TLP were screened using the TCMSP and UniProt databases. HFpEF-related targets were identified using the OMIM and GeneCards databases. Drug-disease intersection targets were obtained via Venny 2.1.0, as well as establishing the "component-target" network and screening out the core active components. Construct a protein-protein interaction network of intersecting targets using the STRING database as well as Cytoscape software and filter the core targets. Gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis of core targets were performed using the Metascape database. The core active components of TLP for HFpEF were quercetin, kaempferol, β-sitosterol, isorhamnetin and hederagenin. The core targets of TLP for HFpEF were JUN, MAPK1, TP53, AKT1, RELA, TNF, MAPK14, and IL16. Gene ontology enrichment analysis obtained 1528 biological processes, 85 cell components, and 140 molecular functions. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis yielded 1940 signaling pathways, mainly involved in lipid and atherosclerosis, regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, HIF-1 signaling pathway, oxidative stress, TNF signaling pathway, and IL-17 signaling pathway. TLP has the characteristics of multi-component, multi-target, and multi-pathway in the treatment of HFpEF. This study lays the foundation for revealing the pharmacodynamic substances and mechanism of TLP in the treatment of HFpEF.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Ephedra Herb in the Treatment of Nephrotic Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 5;2022:9214589. doi: 10.1155/2022/9214589. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35837376 Free PMC article.
-
A network pharmacological-based study of the mechanism of Liuwei Dihuang pill in the treatment of chronic kidney disease.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 May 12;102(19):e33727. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033727. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37171332 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the role and potential mechanism of Liuwei Dihuang Decoction in prostate cancer.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Jul 26;24(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04572-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 39061044 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the mechanism of action of Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder in colorectal cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking studies.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023 Oct;39(2):1107-1127. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2023.2167765. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023. PMID: 36735641 Review.
-
Elucidation of the mechanism of Zhenbao pills for the treatment of spinal cord injury by network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Feb 16;103(7):e36970. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036970. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38363936 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Borlaug BA, Kass DA. Ventricular-vascular interaction in heart failure. Cardiol Clin. 2011;29:447–59. - PubMed
-
- Glezeva N, Baugh JA. Role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and its potential as a therapeutic target. Heart Fail Rev. 2014;19:681–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

