Comparative study between remifentanil (or fentanyl) and dexmedetomidine for the analgesia of rhinoplasty: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 38640315
- PMCID: PMC11029972
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037020
Comparative study between remifentanil (or fentanyl) and dexmedetomidine for the analgesia of rhinoplasty: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Remifentanil (or fentanyl) and dexmedetomidine may have some potential to improve the analgesia of rhinoplasty, and this meta-analysis aims to compare their efficacy for the analgesia of rhinoplasty.
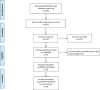
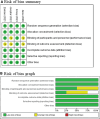
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, EBSCO, and Cochrane Library databases were systematically searched, and we included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) assessing the analgesic effect of remifentanil (or fentanyl) versus dexmedetomidine for rhinoplasty.
Results: Four RCTs were finally included in the meta-analysis. In patients undergoing rhinoplasty, remifentanil (or fentanyl) infusion and dexmedetomidine infusion resulted in similar good patient satisfaction (odd ratio [OR] = 2.71; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.63 to 11.64; P = .18), good surgeon satisfaction (OR = 1.68; 95% CI = 0.02 to 181.40; P = .83), extubation time (mean difference [MD] = 7.56; 95% CI = -11.00 to 26.12; P = .42), recovery time (MD = -2.25; 95% CI = -23.41 to 18.91; P = .83), additional analgesic requirement (OR = 0.16; 95% CI = 0 to 8.65; P = .37) and adverse events (OR = 8.50; 95% CI = 0.47 to 153.30; P = .15).
Conclusions: Remifentanil (or fentanyl) and dexmedetomidine may have comparable analgesia for patients undergoing rhinoplasty.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
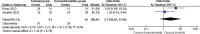
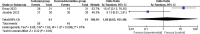
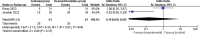
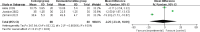
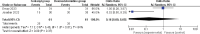

Similar articles
-
Comparison of the effects of remifentanil and dexmedetomidine on surgeon satisfaction with surgical field visualization and intraoperative bleeding during rhinoplasty.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Jan 14;22(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12871-021-01546-9. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 35031005 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dexmedetomidine in combination with fentanyl-based intravenous patient-controlled analgesia on pain attenuation after open gastrectomy in comparison with conventional thoracic epidural and fentanyl-based intravenous patient-controlled analgesia.Int J Med Sci. 2017 Aug 18;14(10):951-960. doi: 10.7150/ijms.20347. eCollection 2017. Int J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28924366 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dexmedetomidine infusion as an analgesic adjuvant during laparoscopic сholecystectomy: a randomized controlled study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2018 Apr 20;18(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12871-018-0508-6. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018. PMID: 29678158 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dexmedetomidine and sufentanil combination versus sufentanil alone for postoperative intravenous patient-controlled analgesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Anesthesiol. 2019 May 18;19(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12871-019-0756-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019. PMID: 31103031 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine versus morphine or fentanyl in the management of children after tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2013 Feb;122(2):114-20. doi: 10.1177/000348941312200207. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2013. PMID: 23534126 Review.
Cited by
-
Minimizing Narcotic Use in Rhinoplasty: An Updated Narrative Review and Protocol.Life (Basel). 2024 Oct 7;14(10):1272. doi: 10.3390/life14101272. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kaplama ME, Ak S, Yukkaldiran A. Is rhinoplasty surgery a risk factor for low back pain among otorhinolaryngologists? Facial Plastic Surg. 2021;37:102–6. - PubMed
-
- Liu RH, Xu LJ, Lee LN. Opioid-sparing pain control after rhinoplasty: Updated Review of the literature. Facial Plast Surg. 2023;39:674–8. - PubMed
-
- Sclafani AP, Kim M, Kjaer K, et al. . Postoperative pain and analgesic requirements after septoplasty and rhinoplasty. Laryngoscope. 2019;129:2020–5. - PubMed
-
- Vaghardoost R, Ahmadi Dahaj A, Haji Mohammad M, et al. . Evaluating the effect of tranexamic acid local injection on the intraoperative bleeding amount and the postoperative edema and ecchymosis in primary rhinoplasty patients: a randomized clinical trial. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2023. - PubMed
-
- Kosucu M, Tugcugil E, Arslan E, et al. . Effects of perioperative magnesium sulfate with controlled hypotension on intraoperative bleeding and postoperative ecchymosis and edema in open rhinoplasty. Am J Otolaryngol. 2020;41:102722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

