An allosteric inhibitor of sirtuin 2 blocks hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA establishment and its transcriptional activity
- PMID: 38641024
- PMCID: PMC12053749
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105888
An allosteric inhibitor of sirtuin 2 blocks hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA establishment and its transcriptional activity
Abstract
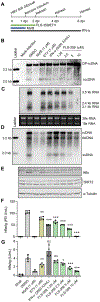
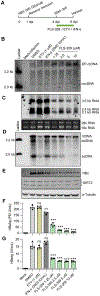
296 million people worldwide are predisposed to developing severe end-stage liver diseases due to chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. HBV forms covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) molecules that persist as episomal DNA in the nucleus of infected hepatocytes and drive viral replication. Occasionally, the HBV genome becomes integrated into host chromosomal DNA, a process that is believed to significantly contribute to circulating HBsAg levels and HCC development. Neither cccDNA accumulation nor expression from integrated HBV DNA are directly targeted by current antiviral treatments. In this study, we investigated the antiviral properties of a newly described allosteric modulator, FLS-359, that targets sirtuin 2 (SIRT2), an NAD+-dependent deacylase. Our results demonstrate that SIRT2 modulation by FLS-359 and by other tool compounds inhibits cccDNA synthesis following de novo infection of primary human hepatocytes and HepG2 (C3A)-NTCP cells, and FLS-359 substantially reduces cccDNA recycling in HepAD38 cells. While pre-existing cccDNA is not eradicated by short-term treatment with FLS-359, its transcriptional activity is substantially impaired, likely through inhibition of viral promoter activities. Consistent with the inhibition of viral transcription, HBsAg production by HepG2.2.15 cells, which contain integrated HBV genomes, is also suppressed by FLS-359. Our study provides further insights on SIRT2 regulation of HBV infection and supports the development of potent SIRT2 inhibitors as HBV antivirals.
Keywords: Antiviral; Hepatitis B virus; SIRT2; Viral transcription; cccDNA synthesis.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests.
Figures

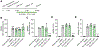



References
-
- Allweiss L, Giersch K, Pirosu A, Volz T, Muench RC, Beran RK, Urban S, Javanbakht H, Fletcher SP, Lutgehetmann M, Dandri M, 2022. Therapeutic shutdown of HBV transcripts promotes reappearance of the SMC5/6 complex and silencing of the viral genome in vivo. Gut 71, 372–381. 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322571. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alter H, Block T, Brown N, Brownstein A, Brosgart C, Chang KM, Chen PJ, Chisari FV, Cohen C, El-Serag H, Feld J, Gish R, Glenn J, Greten T, Guo H, Guo JT, Hoshida Y, Hu J, Kowdley KV, Li W, Liang J, Locarnini S, Lok AS, Mason W, McMahon B, Mehta A, Perrillo R, Revill P, Rice CM, Rinaudo J, Schinazi R, Seeger C, Shetty K, Tavis J, Zoulim F, 2018. A research agenda for curing chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 67, 1127–1131. 10.1002/hep.29509. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

