Comparison of safety and effectiveness of antiretroviral therapy regimens among pregnant women living with HIV at preconception or during pregnancy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized trials
- PMID: 38641597
- PMCID: PMC11031873
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-09303-2
Comparison of safety and effectiveness of antiretroviral therapy regimens among pregnant women living with HIV at preconception or during pregnancy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized trials
Abstract
Background: Mother-to-child transmission is the primary cause of HIV cases among children. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) plays a critical role in preventing mother-to-child transmission and reducing HIV progression, morbidity, and mortality among mothers. However, after more than two decades of ART during pregnancy, the comparative effectiveness and safety of ART medications during pregnancy are unclear, and existing evidence is contradictory. This study aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of different ART regimens among pregnant women living with HIV at preconception or during pregnancy.
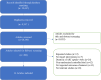
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and Web of Science. We included randomized trials that enrolled pregnant women living with HIV and randomized them to receive ART for at least four weeks. Pairs of reviewers independently completed screening for eligible studies, extracted data, and assessed the risk of bias using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. Our outcomes of interest included low birth weight, stillbirth, preterm birth, mother-to-child transmission of HIV, neonatal death, and congenital anomalies. Network meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects frequentist model, and the certainty of evidence was evaluated using the GRADE approach.
Results: We found 14 eligible randomized trials enrolling 9,561 pregnant women. The median duration of ART uptake ranged from 6.0 to 17.4 weeks. No treatment was statistically better than a placebo in reducing the rate of neonatal mortality, stillbirth, congenital defects, preterm birth, or low birth weight deliveries. Compared to placebo, zidovudine (ZDV)/lamivudine (3TC) and ZDV monotherapy likely reduce mother-to-child transmission (odds ratio (OR): 0.13; 95% CI: 0.05 to 0.31, high-certainty; and OR: 0.50; 95% CI: 0.33 to 0.74, moderate-certainty). Moderate-certainty evidence suggested that ZDV/3TC was associated with decreased odds of stillbirth (OR: 0.47; 95% CI: 0.09 to 2.60).
Conclusions: Our analysis provides high- to moderate-certainty evidence that ZDV/3TC and ZDV are more effective in reducing the odds of mother-to-child transmission, with ZDV/3TC also demonstrating decreased odds of stillbirth. Notably, our findings suggest an elevated odds of stillbirth and preterm birth associated with all other ART regimens.
Keywords: Antiretroviral agents; HIV infection; Infant; Pregnant women; Vertical transmission.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 6;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21735394
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(2):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. PMID: 12076484 Updated.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(2):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510. PMID: 11869666 Updated.
-
Vitamin A supplements for reducing mother-to-child HIV transmission.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 7;9(9):CD003648. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003648.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28880995 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Safety and Efficacy of Antiviral Drugs and Vaccines in Pregnant Women: Insights from Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Integration of Viral Infection Dynamics.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;12(7):782. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12070782. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39066420 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antiretroviral Drugs for Treating Pregnant Women and Preventing HIV Infection in Infants: Recommendations for a Public Health Approach: 2010 Version. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK304944/. Cited 2022. - PubMed

