Can essential fatty acids (EFAs) prevent and ameliorate post-COVID-19 long haul manifestations?
- PMID: 38641607
- PMCID: PMC11027247
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-024-02090-4
Can essential fatty acids (EFAs) prevent and ameliorate post-COVID-19 long haul manifestations?
Abstract
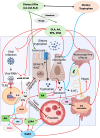
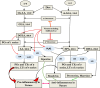
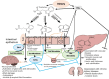
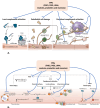
It is hypothesized that COVID-19, post-COVID and post-mRNA COVID-19 (and other related) vaccine manifestations including "long haul syndrome" are due to deficiency of essential fatty acids (EFAs) and dysregulation of their metabolism. This proposal is based on the observation that EFAs and their metabolites can modulate the swift immunostimulatory response of SARS-CoV-2 and similar enveloped viruses, suppress inappropriate cytokine release, possess cytoprotective action, modulate serotonin and bradykinin production and other neurotransmitters, inhibit NF-kB activation, regulate cGAS-STING pathway, modulate gut microbiota, inhibit platelet activation, regulate macrophage and leukocyte function, enhance wound healing and facilitate tissue regeneration and restore homeostasis. This implies that administration of EFAs could be of benefit in the prevention and management of COVID-19 and its associated complications.
Keywords: COVID-19; Eicosanoids; Essential fatty acids; Inflammation; Lipoxin A4; Maresins; Polyunsaturated fatty acids; Protectins; Resolvins; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Pretorius E, Vlok M, Venter C, Bezuidenhout JA, Laubscher GJ, Steenkamp J, Kell DB. Persistent clotting protein pathology in Long COVID/Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) is accompanied by increased levels of antiplasmin. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021;20(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01359-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

