Real-world progression-free survival and overall survival of palbociclib plus endocrine therapy (ET) in Japanese patients with hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer in the first-line or second-line setting: an observational study
- PMID: 38642245
- PMCID: PMC11194199
- DOI: 10.1007/s12282-024-01575-5
Real-world progression-free survival and overall survival of palbociclib plus endocrine therapy (ET) in Japanese patients with hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer in the first-line or second-line setting: an observational study
Abstract
Background: A recent large real-world study conducted in the United States reported the effectiveness of palbociclib plus aromatase inhibitor in HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer (ABC). However, local clinical practice and available medical treatment can vary between Japan and Western countries. Thus, it is important to investigate Japanese real-world data. This observational, multicenter study (NCT05399329) reports the interim analysis of effectiveness of palbociclib plus ET as first-line or second-line treatment for HR+/HER2- ABC by estimating real-world progression-free survival (rwPFS) and overall survival (OS) in Japanese routine clinical practice.
Methods: Real-world clinical outcomes and treatment patterns of palbociclib plus ET were captured using a medical record review of patients diagnosed with HR+/HER2- ABC who had received palbociclib plus ET in the first-line or second-line treatment across 20 sites in Japan. The primary endpoint was rwPFS; secondary endpoints were OS, real-world overall response rate, real-world clinical benefit rate, and chemotherapy-free survival.
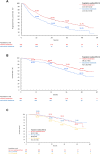
Results: Of the 677 eligible patients, 420 and 257 patients, respectively, had received palbociclib with ET as first-line and second-line treatments. Median rwPFS (95% confidence interval) was 24.5 months (19.9-29.4) for first-line and 14.5 months (10.2-19.0) for second-line treatment groups. Median OS was not reached in the first-line group and was 46.7 months (38.8-not estimated) for the second-line group. The 36-month OS rates for de novo metastasis, treatment-free interval (TFI) ≥ 12 months, and TFI < 12 months were 80.2% (69.1-87.7), 82.0% (70.7-89.3), and 66.0% (57.9-72.9), respectively.
Conclusion: The addition of palbociclib to ET was effective for treating HR+/HER2- ABC in Japanese routine clinical practice.
Keywords: Advanced breast cancer; CDK4/6 inhibitors; Palbociclib; Real-world evidence.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TY reports honoraria from AstraZeneca, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly, MSD, and Pfizer. SN reports honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, MSD, Taiho, Chugai, and Pfizer. MaHa reports honoraria from Eli Lilly and Pfizer. KW reports honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Shionogi, Kyowa-Kirin, Nippon-Kayaku, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Taiho, Chugai, and Pfizer. TN reports honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Taiho, Chugai, and Pfizer. HiMa reports honoraria from Eli Lilly, Chugai, and Pfizer. TS reports honoraria from Chugai, Novartis, MSD, Taiho, Eisai, Maruho, PDRadiopahrma, Nippon-Kayaku, Kyowa-Kirin, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Daiichi -Sankyo and Pfizer; and institutional support from Taiho.MY reports honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Kyowa-Kirin, Nippon-Kayaku, Eli Lilly, Taiho, Chugai, and Pfizer. NK and KT are employees of Pfizer Inc. NK is stockholders in Pfizer Inc. NM reports honoraria from Chugai, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, and Daiichi -Sankyo; and institutional support from Chugai, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Daiichi-Sankyo, MSD, Eisai, Novartis, Sanofi, KyowaKirin, and Nippon Kayaku. TO, MT, DT, MH, HY, NM, HY, CO, and MI have no disclosures.
Figures

References
-
- Agnese D, Burns J, Giordano SH, Kumar R. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. Breast cancer. 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

