Bacterial extracellular vesicles: biotechnological perspective for enhanced productivity
- PMID: 38642254
- PMCID: PMC11032300
- DOI: 10.1007/s11274-024-03963-7
Bacterial extracellular vesicles: biotechnological perspective for enhanced productivity
Abstract
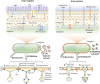
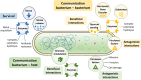
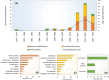
Bacterial extracellular vesicles (BEVs) are non-replicative nanostructures released by Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria as a survival mechanism and inter- and intraspecific communication mechanism. Due to BEVs physical, biochemical, and biofunctional characteristics, there is interest in producing and using them in developing new therapeutics, vaccines, or delivery systems. However, BEV release is typically low, limiting their application. Here, we provide a biotechnological perspective to enhance BEV production, highlighting current strategies. The strategies include the production of hypervesiculating strains through gene modification, bacteria culture under stress conditions, and artificial vesicles production. We discussed the effect of these production strategies on BEVs types, morphology, composition, and activity. Furthermore, we summarized general aspects of BEV biogenesis, functional capabilities, and applications, framing their current importance and the need to produce them in abundance. This review will expand the knowledge about the range of strategies associated with BEV bioprocesses to increase their productivity and extend their application possibilities.
Keywords: Artificial bacterial vesicles; Bacterial extracellular vesicles (BEVs); Hypervesiculation strains; Vesiculation cellular response to stress.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unveiling clinical applications of bacterial extracellular vesicles as natural nanomaterials in disease diagnosis and therapeutics.Acta Biomater. 2024 May;180:18-45. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.04.022. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Acta Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38641182 Review.
-
Correlation between bacterial extracellular vesicles and antibiotics: A potentially antibacterial strategy.Microb Pathog. 2023 Aug;181:106167. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106167. Epub 2023 May 22. Microb Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37224984 Review.
-
Multiple Particle Tracking: A Method for Probing Biologically Relevant Mobility of Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2843:137-152. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4055-5_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39141298
-
The tremendous biomedical potential of bacterial extracellular vesicles.Trends Biotechnol. 2022 Oct;40(10):1173-1194. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2022.03.005. Epub 2022 May 14. Trends Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35581020 Review.
-
Analyzing bacterial extracellular vesicles in human body fluids by orthogonal biophysical separation and biochemical characterization.Nat Protoc. 2020 Jan;15(1):40-67. doi: 10.1038/s41596-019-0236-5. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Nat Protoc. 2020. PMID: 31776460
Cited by
-
Melioidosis molecular diagnostics: An update.Virulence. 2025 Dec;16(1):2505698. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2025.2505698. Epub 2025 Jun 14. Virulence. 2025. PMID: 40515758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biological activity and potential of probiotics-derived extracellular vesicles as postbiotics in modulating microbiota-host communication.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 16;23(1):349. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03435-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40380331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilization of Probiotic-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Postbiotics and Their Role in Mental Health Therapeutics.Food Sci Anim Resour. 2024 Nov;44(6):1252-1265. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2024.e92. Epub 2024 Nov 1. Food Sci Anim Resour. 2024. PMID: 39554832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioprocessing strategies for enhanced probiotic extracellular vesicle production: culture condition modulation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 30;12:1441552. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1441552. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39280339 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles and Antimicrobial Peptides: A Synergistic Approach to Overcome Antimicrobial Resistance.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Apr 19;14(4):414. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14040414. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aktar S, Okamoto Y, Ueno S, Tahara YO, Imaizumi M, Shintani M, Miyata M, Futamata H, Nojiri H, Tashiro Y. Incorporation of plasmid DNA in to bacterial membrane vesicles by peptidoglycan defects in Escherichia coli. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:747606. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.747606. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alfini R, Brunelli B, Bartolini E, Carducci M, Luzzi E, Ferlicca F, Buccato S, Galli B, Lo Surdo P, Scarselli M, Romagnoli G, Cartocci E, Maione D, Savino S, Necchi F, Delany I, Micoli F. Investigating the role of antigen orientation on the immune response elicited by Neisseria meningitidis factor H binding protein on GMMA. Vaccines. 2022 doi: 10.3390/vaccines10081182. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alvarez CS, Giménez R, Cañas MA, Vera R, Díaz-Garrido N, Badia J, Baldomà L. Extracellular vesicles and soluble factors secreted by Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 and ECOR63 protect against enteropathogenic E. coli-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction. BMC Microbiol. 2019;19(1):1–12. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1534-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CVU 1102921/Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología
- CVU 1102922/Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología
- CF-2023-I-1248/Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología
- CF-2023-I-1549/Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología
- IN-211422/Dirección General de Asuntos del Personal Académico, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

