The Immunology of Psoriasis-Current Concepts in Pathogenesis
- PMID: 38642273
- PMCID: PMC11193704
- DOI: 10.1007/s12016-024-08991-7
The Immunology of Psoriasis-Current Concepts in Pathogenesis
Abstract
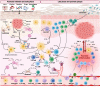
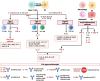
Psoriasis is one of the most common inflammatory skin diseases with a chronic, relapsing-remitting course. The last decades of intense research uncovered a pathological network of interactions between immune cells and other types of cells in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Emerging evidence indicates that dendritic cells, TH17 cells, and keratinocytes constitute a pathogenic triad in psoriasis. Dendritic cells produce TNF-α and IL-23 to promote T cell differentiation toward TH17 cells that produce key psoriatic cytokines IL-17, IFN-γ, and IL-22. Their activity results in skin inflammation and activation and hyperproliferation of keratinocytes. In addition, other cells and signaling pathways are implicated in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, including TH9 cells, TH22 cells, CD8+ cytotoxic cells, neutrophils, γδ T cells, and cytokines and chemokines secreted by them. New insights from high-throughput analysis of lesional skin identified novel signaling pathways and cell populations involved in the pathogenesis. These studies not only expanded our knowledge about the mechanisms of immune response and the pathogenesis of psoriasis but also resulted in a revolution in the clinical management of patients with psoriasis. Thus, understanding the mechanisms of immune response in psoriatic inflammation is crucial for further studies, the development of novel therapeutic strategies, and the clinical management of psoriasis patients. The aim of the review was to comprehensively present the dysregulation of immune response in psoriasis with an emphasis on recent findings. Here, we described the role of immune cells, including T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, neutrophils, monocytes, mast cells, and innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), as well as non-immune cells, including keratinocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and platelets in the initiation, development, and progression of psoriasis.
Keywords: Immune response; Keratinocyte; Psoriasis; Skin inflammation; TH17 cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Calcipotriol and betamethasone dipropionate exert additive inhibitory effects on the cytokine expression of inflammatory dendritic cell-Th17 cell axis in psoriasis.J Dermatol Sci. 2016 Mar;81(3):153-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2015.12.009. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Dermatol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26794805
-
Pathophysiology of psoriasis: recent advances on IL-23 and Th17 cytokines.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2007 Dec;9(6):461-7. doi: 10.1007/s11926-007-0075-1. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2007. PMID: 18177599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-29 induces epithelial production of CXCR3A ligands and T-cell infiltration.J Mol Med (Berl). 2016 Apr;94(4):391-400. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1367-y. Epub 2015 Nov 26. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016. PMID: 26612594
-
Psoriasis and other Th17-mediated skin diseases.J UOEH. 2010 Dec 1;32(4):317-28. doi: 10.7888/juoeh.32.317. J UOEH. 2010. PMID: 21226422 Review.
-
Cellular sources of IL-17 in psoriasis: a paradigm shift?Exp Dermatol. 2014 Nov;23(11):799-803. doi: 10.1111/exd.12487. Exp Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 25039885 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic effects and mechanisms of Fufang Longdan mixture on metabolic syndrome with psoriasis via miR-29a-5p/IGF-1R axis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 9;16:1585369. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1585369. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40417212 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Orally Administered East Asian Herbal Medicine Combined with Narrowband Ultraviolet B against Psoriasis: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis and Network Analysis.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 13;16(16):2690. doi: 10.3390/nu16162690. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39203826 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of small molecule drugs in the treatment of pityriasis rubra pilaris-A systematic review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 25;12:1544197. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1544197. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40093023 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Shared Diagnostic Genes in IBD and Psoriasis through Bioinformatics and Experimental Assays.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Mar 3;22(7):1680-1697. doi: 10.7150/ijms.107018. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40093802 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary Interleukins as Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Psoriasis: Advances and Challenges in Diagnosis and Monitoring.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jun 29;61(7):1180. doi: 10.3390/medicina61071180. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40731810 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

