Targeting EED as a key PRC2 complex mediator toward novel epigenetic therapeutics
- PMID: 38642703
- PMCID: PMC11416859
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.103986
Targeting EED as a key PRC2 complex mediator toward novel epigenetic therapeutics
Abstract
EED within the PRC2 complex is crucial for chromatin regulation particularly in tumor development, making its inhibition a promising epigenetic therapeutic strategy. Significant advancement in PRC2 inhibitor development has been achieved with an approved EZH2 inhibitor in the market and with others in the clinical trials. However, current EZH2 inhibitors are limited to specific blood cancers and encounter therapeutic resistance. EED stabilizes PRC2 complex and enhances its activity through unique allosteric mechanisms, thereby acting as both a scaffold protein and a recognizer of H3K27me3 making it an attractive drug target. This review provides an overview of epigenetic therapeutic strategies targeting EED, including allosteric inhibitors, PPI inhibitors, and PROTACs, together with brief discussions on the relevant challenges, opportunities, and future directions.
Keywords: EED; PRC2; PROTACs; cancer therapy; epigenetic therapeutics; protein–protein interaction modulators.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest associated with this article.
Figures
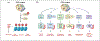


References
-
- Piunti A, Shilatifard A. The roles of Polycomb repressive complexes in mammalian development and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:326–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

