miR-29b-3p regulates cardiomyocytes pyroptosis in CVB3-induced myocarditis through targeting DNMT3A
- PMID: 38643118
- PMCID: PMC11031889
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-024-00576-8
miR-29b-3p regulates cardiomyocytes pyroptosis in CVB3-induced myocarditis through targeting DNMT3A
Abstract
Background: Viral myocarditis (VMC) is a disease resulting from viral infection, which manifests as inflammation of myocardial cells. Until now, the treatment of VMC is still a great challenge for clinicians. Increasing studies indicate the participation of miR-29b-3p in various diseases. According to the transcriptome sequencing analysis, miR-29b-3p was markedly upregulated in the viral myocarditis model. The purpose of this study was to investigate the role of miR-29b-3p in the progression of VMC.
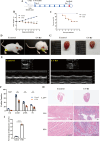
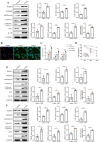
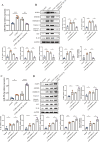
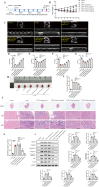
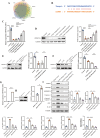
Methods: We used CVB3 to induce primary cardiomyocytes and mice to establish a model of viral myocarditis. The purity of primary cardiomyocytes was identified by immunofluorescence. The cardiac function of mice was detected by Vevo770 imaging system. The area of inflammatory infiltration in heart tissue was shown by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. The expression of miR-29b-3p and DNMT3A was detected by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The expression of a series of pyroptosis-related proteins was detected by western blot. The role of miR-29b-3p/DNMT3A in CVB3-induced pyroptosis of cardiomyocytes was studied in this research.
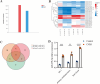
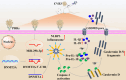
Results: Our data showed that the expression of miR-29b-3p was upregulated in CVB3-induced cardiomyocytes and heart tissues in mice. To explore the function of miR-29b-3p in CVB3-induced VMC, we conducted in vivo experiments by knocking down the expression of miR-29b-3p using antagomir. We then assessed the effects on mice body weight, histopathology changes, myocardial function, and cell pyroptosis in heart tissues. Additionally, we performed gain/loss-of-function experiments in vitro to measure the levels of pyroptosis in primary cardiomyocytes. Through bioinformatic analysis, we identified DNA methyltransferases 3A (DNMT3A) as a potential target gene of miR-29b-3p. Furthermore, we found that the expression of DNMT3A can be modulated by miR-29b-3p during CVB3 infection.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate a correlation between the expression of DNMT3A and CVB3-induced pyroptosis in cardiomyocytes. These findings unveil a previously unidentified mechanism by which CVB3 induces cardiac injury through the regulation of miR-29b-3p/DNMT3A-mediated pyroptosis.
Keywords: CVB3; DNMT3A; Pyroptosis; Viral myocarditis; miR-29b-3p.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-30a-5p silencing polarizes macrophages toward M2 phenotype to alleviate cardiac injury following viral myocarditis by targeting SOCS1.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 Apr 1;320(4):H1348-H1360. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00431.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33416455
-
Overexpression of microRNA-133b reduces myocardial injuries in children with viral myocarditis by targeting Rab27B gene.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2017 Oct 31;63(10):80-86. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2017.63.10.13. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2017. PMID: 29096746
-
LncRNA MALAT1 to Enhance Pyroptosis in Viral Myocarditis Through UPF1-Mediated SIRT6 mRNA Decay and Wnt-β-Catenin Signal Pathway.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Dec;24(12):1439-1454. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09922-w. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39367210
-
The Role of MicroRNA in the Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Viral Myocarditis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 11;25(20):10933. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010933. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights gained from cellular landscape changes in myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy.Heart Fail Rev. 2024 Sep;29(5):883-907. doi: 10.1007/s10741-024-10406-w. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Heart Fail Rev. 2024. PMID: 38896377 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs in long COVID: roles, diagnostic biomarker potential and detection.Hum Genomics. 2025 Aug 13;19(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s40246-025-00810-0. Hum Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40804645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircPTPN11 inhibits the replication of Coxsackievirus B5 through regulating the IFN-I pathway by targeting miR-152-3p/SIRPA axis.Virus Res. 2024 Dec;350:199508. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2024.199508. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Virus Res. 2024. PMID: 39647532 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modification regulates the ligamentum flavum hypertrophy through miR-335-3p/SERPINE2/β-catenin signaling pathway.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jan 3;30(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00660-z. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 39754051 Free PMC article.
-
Pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases: roles, mechanisms, and clinical implications.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Aug 4;12:1629016. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1629016. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40832143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism Actions of Coniferyl Alcohol in Improving Cardiac Dysfunction in Renovascular Hypertension Studied by Experimental Verification and Network Pharmacology.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 19;25(18):10063. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810063. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caforio AL, Pankuweit S, Arbustini E, Basso C, Gimeno-Blanes J, Felix SB, et al. Current state of knowledge on aetiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy of myocarditis: a position statement of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(33):2636–2648. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht210. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

