Scalable protein production by Komagataella phaffii enabled by ARS plasmids and carbon source-based selection
- PMID: 38643119
- PMCID: PMC11031860
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-024-02368-3
Scalable protein production by Komagataella phaffii enabled by ARS plasmids and carbon source-based selection
Abstract
Background: Most recombinant Komagataella phaffii (Pichia pastoris) strains for protein production are generated by genomic integration of expression cassettes. The clonal variability in gene copy numbers, integration loci and consequently product titers limit the aptitude for high throughput applications in drug discovery, enzyme engineering or most comparative analyses of genetic elements such as promoters or secretion signals. Circular episomal plasmids with an autonomously replicating sequence (ARS), an alternative which would alleviate some of these limitations, are inherently unstable in K. phaffii. Permanent selection pressure, mostly enabled by antibiotic resistance or auxotrophy markers, is crucial for plasmid maintenance and hardly scalable for production. The establishment and use of extrachromosomal ARS plasmids with key genes of the glycerol metabolism (glycerol kinase 1, GUT1, and triosephosphate isomerase 1, TPI1) as selection markers was investigated to obtain a system with high transformation rates that can be directly used for scalable production processes in lab scale bioreactors.
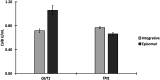
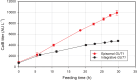
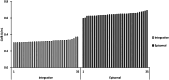
Results: In micro-scale deep-well plate experiments, ARS plasmids employing the Ashbya gossypii TEF1 (transcription elongation factor 1) promoter to regulate transcription of the marker gene were found to deliver high transformation efficiencies and the best performances with the reporter protein (CalB, lipase B of Candida antarctica) for both, the GUT1- and TPI1-based, marker systems. The GUT1 marker-bearing strain surpassed the reference strain with integrated expression cassette by 46% upon re-evaluation in shake flask cultures regarding CalB production, while the TPI1 system was slightly less productive compared to the control. In 5 L bioreactor methanol-free fed-batch cultivations, the episomal production system employing the GUT1 marker led to 100% increased CalB activity in the culture supernatant compared to integration construct.
Conclusions: For the first time, a scalable and methanol-independent expression system for recombinant protein production for K. phaffii using episomal expression vectors was demonstrated. Expression of the GUT1 selection marker gene of the new ARS plasmids was refined by employing the TEF1 promoter of A. gossypii. Additionally, the antibiotic-free marker toolbox for K. phaffii was expanded by the TPI1 marker system, which proved to be similarly suited for the use in episomal plasmids as well as integrative expression constructs for the purpose of recombinant protein production.
Keywords: GUT1; Komagataella phaffii; Pichia pastoris; TPI1; Carbon source marker; Episomal ARS plasmid; Lipase CalB; Methanol-free bioprocesses.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Higgins DR, Cregg JM. Introduction to Pichia pastoris. In: Molecular Biotechnology. 1998. p. 1–15. 10.1385/0-89603-421-6:1. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

