NLRP inflammasomes in health and disease
- PMID: 38644450
- PMCID: PMC11033252
- DOI: 10.1186/s43556-024-00179-x
NLRP inflammasomes in health and disease
Abstract
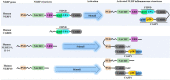
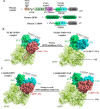
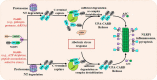
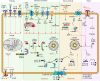
NLRP inflammasomes are a group of cytosolic multiprotein oligomer pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) involved in the recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) produced by infected cells. They regulate innate immunity by triggering a protective inflammatory response. However, despite their protective role, aberrant NLPR inflammasome activation and gain-of-function mutations in NLRP sensor proteins are involved in occurrence and enhancement of non-communicating autoimmune, auto-inflammatory, and neurodegenerative diseases. In the last few years, significant advances have been achieved in the understanding of the NLRP inflammasome physiological functions and their molecular mechanisms of activation, as well as therapeutics that target NLRP inflammasome activity in inflammatory diseases. Here, we provide the latest research progress on NLRP inflammasomes, including NLRP1, CARD8, NLRP3, NLRP6, NLRP7, NLRP2, NLRP9, NLRP10, and NLRP12 regarding their structural and assembling features, signaling transduction and molecular activation mechanisms. Importantly, we highlight the mechanisms associated with NLRP inflammasome dysregulation involved in numerous human auto-inflammatory, autoimmune, and neurodegenerative diseases. Overall, we summarize the latest discoveries in NLRP biology, their forming inflammasomes, and their role in health and diseases, and provide therapeutic strategies and perspectives for future studies about NLRP inflammasomes.
Keywords: Auto-inflammatory; Autoimmune; Health and disease; NLRP inflammasome; Neurological disorders; Therapeutic inhibitor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022YFC2304102/Key Technologies Research and Development Program
- 31971129/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82272301/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022i01020025/Anhui Provincial Key Research and Development Project
- WK9100000001/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
