Crtc1 deficiency protects against sepsis-associated acute lung injury through activating akt signaling pathway
- PMID: 38644501
- PMCID: PMC11034098
- DOI: 10.1186/s12950-024-00385-y
Crtc1 deficiency protects against sepsis-associated acute lung injury through activating akt signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Interplay between systemic inflammation and programmed cell death contributes to the pathogenesis of acute lung injury (ALI). cAMP-regulated transcriptional coactivator 1 (CRTC1) has been involved in the normal function of the pulmonary system, but its role in ALI remains unclear.
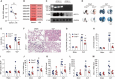
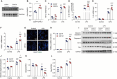
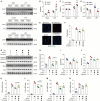
Methods and results: We generated a Crtc1 knockout (KO; Crtc1-/-) mouse line. Sepsis-induced ALI was established by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) for 24 h. The data showed that Ctrc1 KO substantially ameliorated CLP-induced ALI phenotypes, including improved lung structure destruction, reduced pulmonary vascular permeability, diminished levels of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, compared with the wildtype mice. Consistently, in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated RAW264.7 cells, Crtc1 knockdown significantly inhibited the expression of inflammatory effectors, including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and CXCL1, whereas their expressions were significantly enhanced by Crtc1 overexpression. Moreover, both Crtc1 KO in mice and its knockdown in RAW264.7 cells dramatically reduced TUNEL-positive cells and the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins. In contrast, Crtc1 overexpression led to an increase in the pro-apoptotic proteins and LPS-induced TUNEL-positive cells. Mechanically, we found that the phosphorylation of Akt was significantly enhanced by Crtc1 knockout or knockdown, but suppressed by Crtc1 overexpression. Administration of Triciribine, an Akt inhibitor, substantially blocked the protection of Crtc1 knockdown on LPS-induced inflammation and cell death in RAW264.7 cells.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates that CRTC1 contribute to the pathological processes of inflammation and apoptosis in sepsis-induced ALI, and provides mechanistic insights into the molecular function of CRTC1 in the lung. Targeting CRTC1 would be a promising strategy to treat sepsis-induced ALI in clinic.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Apoptosis; Crtc1; Inflammation; Sepsis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Serinc2 deficiency causes susceptibility to sepsis-associated acute lung injury.J Inflamm (Lond). 2022 Jul 7;19(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12950-022-00306-x. J Inflamm (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35799194 Free PMC article.
-
CircC3P1 attenuated pro-inflammatory cytokine production and cell apoptosis in acute lung injury induced by sepsis through modulating miR-21.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Oct;24(19):11221-11229. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15685. Epub 2020 Aug 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32846020 Free PMC article.
-
ERRα protects against sepsis-induced acute lung injury in rats.Mol Med. 2023 Jun 20;29(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00670-1. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37340376 Free PMC article.
-
Heat Shock Protein A12B Protects Vascular Endothelial Cells Against Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(1):156-168. doi: 10.1159/000477308. Epub 2017 May 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28535510
-
Overexpressing six-transmembrane protein of prostate 2 (STAMP2) alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury probably by hindering M1 macrophage polarization via the NF-κB pathway.Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2023;61(1):34-46. doi: 10.5603/FHC.a2022.0032. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2023. PMID: 36583372
References
Grants and funding
- 82370392; 82070231/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022A1515012517/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- RCJC20210706091947009/Science, Technology and Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality
- B2302026/Medical Research Project from Shenzhen Academy of Medical Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

