Lipid metabolism in tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells: perspective to precision immunotherapy
- PMID: 38644503
- PMCID: PMC11034130
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-024-00588-8
Lipid metabolism in tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells: perspective to precision immunotherapy
Abstract
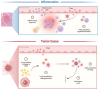
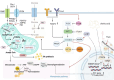
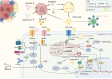
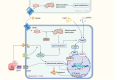
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are essential to the negative regulation of the immune system, as they avoid excessive inflammation and mediate tumor development. The abundance of Tregs in tumor tissues suggests that Tregs may be eliminated or functionally inhibited to stimulate antitumor immunity. However, immunotherapy targeting Tregs has been severely hampered by autoimmune diseases due to the systemic elimination of Tregs. Recently, emerging studies have shown that metabolic regulation can specifically target tumor-infiltrating immune cells, and lipid accumulation in TME is associated with immunosuppression. Nevertheless, how Tregs actively regulate metabolic reprogramming to outcompete effector T cells (Teffs), and how lipid metabolic reprogramming contributes to the immunomodulatory capacity of Tregs have not been fully discussed. This review will discuss the physiological processes by which lipid accumulation confers a metabolic advantage to tumor-infiltrating Tregs (TI-Tregs) and amplifies their immunosuppressive functions. Furthermore, we will provide a summary of the driving effects of various metabolic regulators on the metabolic reprogramming of Tregs. Finally, we propose that targeting the lipid metabolism of TI-Tregs could be efficacious either alone or in conjunction with immune checkpoint therapy.
Keywords: Immunosuppression; Lipid metabolism; Metabolic competition; Metabolic regulatory switches; Tregs; Tumor therapies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting the metabolism of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells.Trends Immunol. 2023 Aug;44(8):598-612. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2023.06.001. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Trends Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37442660 Review.
-
Infiltrating treg reprogramming in the tumor immune microenvironment and its optimization for immunotherapy.Biomark Res. 2024 Sep 4;12(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00630-9. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39227959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intratumoral stem-like CCR4+ regulatory T cells orchestrate the immunosuppressive microenvironment in HCC associated with hepatitis B.J Hepatol. 2022 Jan;76(1):148-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.08.029. Epub 2021 Sep 12. J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 34689996
-
Tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells as targets of cancer immunotherapy.Cancer Cell. 2023 Mar 13;41(3):450-465. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.02.014. Cancer Cell. 2023. PMID: 36917950 Review.
-
Treg programming and therapeutic reprogramming in cancer.Immunology. 2019 Jul;157(3):198-209. doi: 10.1111/imm.13058. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Immunology. 2019. PMID: 30866047 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic targeting of regulatory T cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma: new horizons in immunotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2024 Dec 19;23(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02193-7. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39696340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol effects on the tumor immune microenvironment: from fundamental concepts to mechanisms and implications.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 9;15:1579054. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1579054. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40270603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymphatic dissemination of HPV-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: underlying mechanisms and treatment innovations.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 2;16:1601572. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1601572. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40529367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rewiring lipid metabolism to enhance immunotherapy efficacy in melanoma: a frontier in cancer treatment.Front Oncol. 2025 May 1;15:1519592. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1519592. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40376583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis and Cellular Experimental Validation Identify Lipoprotein Lipase Gene as a Novel Biomarker for Tumorigenesis and Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Biology (Basel). 2025 May 19;14(5):566. doi: 10.3390/biology14050566. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427755 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

