This is a preprint.
De novo variants in the non-coding spliceosomal snRNA gene RNU4-2 are a frequent cause of syndromic neurodevelopmental disorders
- PMID: 38645094
- PMCID: PMC11030480
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.04.07.24305438
De novo variants in the non-coding spliceosomal snRNA gene RNU4-2 are a frequent cause of syndromic neurodevelopmental disorders
Update in
-
De novo variants in the RNU4-2 snRNA cause a frequent neurodevelopmental syndrome.Nature. 2024 Aug;632(8026):832-840. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07773-7. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38991538 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Around 60% of individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders (NDD) remain undiagnosed after comprehensive genetic testing, primarily of protein-coding genes1. Increasingly, large genome-sequenced cohorts are improving our ability to discover new diagnoses in the non-coding genome. Here, we identify the non-coding RNA RNU4-2 as a novel syndromic NDD gene. RNU4-2 encodes the U4 small nuclear RNA (snRNA), which is a critical component of the U4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP complex of the major spliceosome2. We identify an 18 bp region of RNU4-2 mapping to two structural elements in the U4/U6 snRNA duplex (the T-loop and Stem III) that is severely depleted of variation in the general population, but in which we identify heterozygous variants in 119 individuals with NDD. The vast majority of individuals (77.3%) have the same highly recurrent single base-pair insertion (n.64_65insT). We estimate that variants in this region explain 0.41% of individuals with NDD. We demonstrate that RNU4-2 is highly expressed in the developing human brain, in contrast to its contiguous counterpart RNU4-1 and other U4 homologs, supporting RNU4-2's role as the primary U4 transcript in the brain. Overall, this work underscores the importance of non-coding genes in rare disorders. It will provide a diagnosis to thousands of individuals with NDD worldwide and pave the way for the development of effective treatments for these individuals.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests NW receives research funding from Novo Nordisk and has consulted for ArgoBio studio. SJS receives research funding from BioMarin Pharmaceutical. AODL is on the scientific advisory board for Congenica, was a paid consultant for Tome Biosciences and Ono Pharma USA Inc., and received reagents from PacBio to support rare disease research. HLR has received support from Illumina and Microsoft to support rare disease gene discovery and diagnosis. MHW has consulted for Illumina and Sanofi and received speaking honoraria from Illumina and GeneDx. SBM is an advisor for BioMarin, Myome and Tenaya Therapeutics. SMS has received honoraria for educational events or advisory boards from Angelini Pharma, Biocodex, Eisai, Zogenix/UCB and institutional contributions for advisory boards, educational events or consultancy work from Eisai, Jazz/GW Pharma, Stoke Therapeutics, Takeda, UCB and Zogenix. The Department of Molecular and Human Genetics at Baylor College of Medicine receives revenue from clinical genetic testing completed at Baylor Genetics Laboratories. JMMH is a full-time employee of Novo Nordisk and holds shares in Novo Nordisk A/S. DGM is a paid consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Insitro, and Overtone Therapeutics and receives research support from Microsoft.
Figures
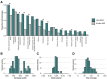

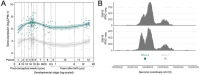
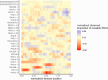
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- UM1 HG008900/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007709/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011762/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011755/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG010217/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R21 HG012397/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007942/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS134358/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG011746/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH129751/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH122681/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG009141/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR083505/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS115052/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS131172/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011745/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH111662/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH122681/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS106845/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103555/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
